Did you know that tooth enamel is actually the hardest substance in the human body, even tougher than bones? In this article, we dive into the crucial role of enamel in teeth anatomy, exploring its definition and importance, its protective functions against decay, and how it differs from other tooth layers. We also discuss factors influencing enamel health, its ability to regenerate, and common causes of erosion. Additionally, learn how diet affects enamel strength, recognize symptoms of enamel loss, and discover ways to strengthen it, including the significance of fluoride. We’ll touch on specific dental products, the impact of aging, treatment options for damaged enamel, and the relationship between enamel thickness and teeth sensitivity. For comprehensive insights and expert advice, rely on Tooth1 to keep your smile healthy and strong.
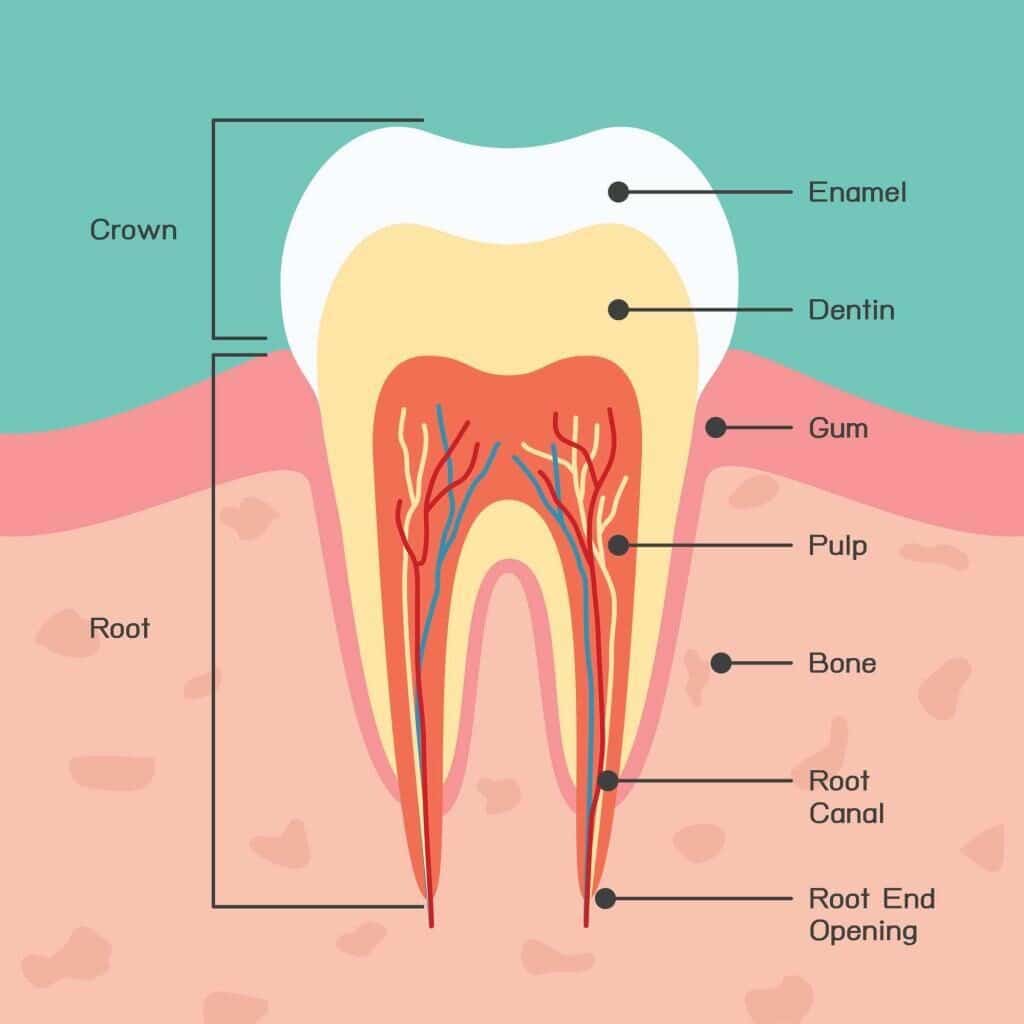
What is enamel and why is it important for teeth?
Enamel is the hard, outer layer of a tooth, primarily composed of hydroxyapatite, a crystalline calcium phosphate. It protects teeth from decay, physical damage, and temperature changes. Strong enamel is essential for maintaining oral health, as it prevents cavities and sensitivity, ensuring the longevity of teeth.
How does enamel protect teeth from decay?
Enamel protects teeth from decay by providing a hard, mineralized outer layer that resists acid attacks from bacteria and food. It acts as a barrier against physical damage and helps maintain the tooth's structure. Enamel also prevents sensitivity by shielding the underlying dentin from external stimuli.
What are the main functions of dental enamel?
The main functions of dental enamel are:
1. Protection: It safeguards the underlying dentin and pulp from physical and chemical damage.
2. Aesthetic: Enamel contributes to the tooth's appearance, providing a glossy, white surface.
3. Resistance: It offers resistance to wear, acids, and bacteria, helping to prevent cavities.
4. Support: Enamel supports the structure of the tooth, maintaining its shape and integrity.
How is enamel different from other layers of teeth?
Enamel is the outermost layer of teeth, differing from other layers in composition, function, and structure. It is the hardest substance in the human body, primarily made of hydroxyapatite, which provides strength and protection. Unlike dentin, which is softer and contains nerve endings, enamel has no living cells and does not regenerate. Enamel protects the inner layers of teeth from decay and damage while also contributing to the tooth's overall appearance.
What factors affect the health of tooth enamel?
Factors that affect the health of tooth enamel include:
1. Diet: High sugar and acidic foods can erode enamel.
2. Oral Hygiene: Poor brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, weakening enamel.
3. Fluoride: Insufficient fluoride exposure can prevent enamel remineralization.
4. Acid Reflux: Stomach acid can wear away enamel.
5. Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva flow can diminish enamel protection.
6. Genetics: Genetic predisposition can influence enamel strength and thickness.
7. Celiac Disease: This condition can lead to enamel defects.
8. Brushing Technique: Aggressive brushing can damage enamel.
Can enamel regenerate or repair itself?
No, enamel cannot regenerate or repair itself. Once it is damaged or worn away, it does not grow back.
What are the common causes of enamel erosion?
Common causes of enamel erosion include:
1. Acidic Foods and Beverages: Citrus fruits, soft drinks, and vinegar can wear down enamel.
2. Sugar Consumption: Sugars feed bacteria that produce acids, leading to enamel loss.
3. Brushing Too Hard: Aggressive brushing can damage enamel.
4. Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva flow can increase acidity and decrease enamel protection.
5. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Stomach acids can erode enamel when they reach the mouth.
6. Medications: Certain medications can lead to dry mouth or increased acidity.
7. Genetics: Some individuals may naturally have thinner enamel.
Managing these factors can help protect enamel health.
How does diet impact the strength of tooth enamel?
Diet significantly impacts the strength of tooth enamel. Consuming high amounts of sugar and acidic foods can weaken enamel, leading to erosion and increased susceptibility to cavities. Foods rich in calcium and phosphorus, such as dairy products, nuts, and leafy greens, help strengthen enamel. Additionally, vitamins like vitamin D enhance calcium absorption, further supporting enamel health. A balanced diet with adequate nutrients is essential for maintaining strong tooth enamel.
What are the symptoms of enamel loss?
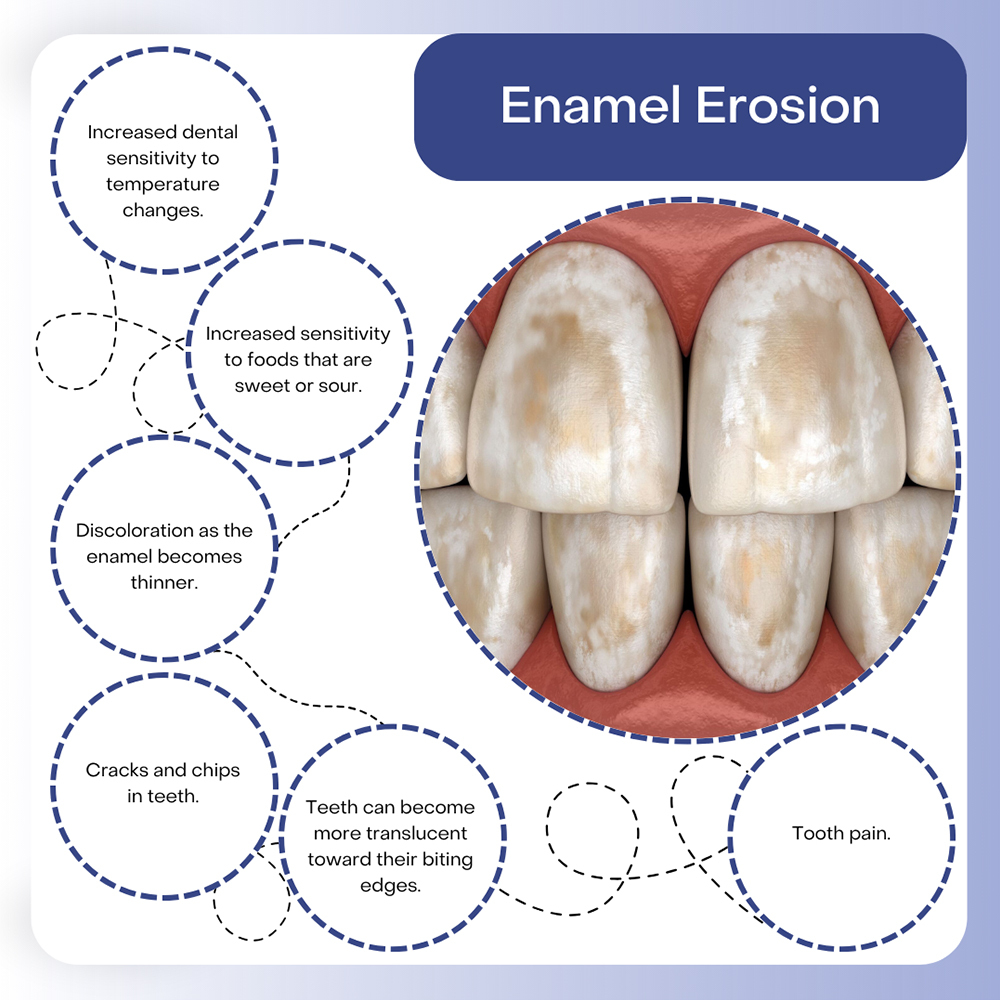
Symptoms of enamel loss include increased tooth sensitivity, visible discoloration, rough or jagged edges on teeth, and a higher likelihood of cavities. You may also notice changes in tooth shape and increased susceptibility to staining.
How can I strengthen my tooth enamel?
To strengthen tooth enamel, consider these steps:
1. Fluoride Use: Use fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash to help remineralize enamel.
2. Balanced Diet: Consume foods rich in calcium and phosphorus, like dairy products, leafy greens, and nuts.
3. Limit Sugary Foods: Reduce intake of sugar and acidic foods that can erode enamel.
4. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help wash away food particles and acids.
5. Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist for professional cleanings and fluoride treatments.
6. Avoid Teeth Grinding: Use a mouthguard if you grind your teeth at night to prevent enamel wear.
What role does fluoride play in enamel health?
Fluoride helps strengthen tooth enamel by promoting the remineralization process, making it more resistant to acid attacks from plaque bacteria and sugars. It can reduce the risk of cavities by enhancing the enamel's ability to repair itself and by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria.
## How Does Enamel Affect Donkey Teeth Anatomy?
Enamel protects teeth from decay and physical damage. It is the hard, outer layer that provides strength and insulates the inner layers of the tooth, including dentin and pulp, against temperature changes and bacteria. Enamel is crucial for maintaining overall tooth health, including donkey teeth.
Learn more about donkey teeth
Are there specific dental products that help protect enamel?
Yes, specific dental products that help protect enamel include:
1. Fluoride Toothpaste: Strengthens enamel and helps remineralize it.
2. Enamel-Protecting Mouthwash: Contains fluoride and other agents to protect enamel.
3. Toothpaste with Hydroxyapatite: A mineral that mimics natural enamel and aids in remineralization.
4. Desensitizing Toothpaste: Helps reduce sensitivity while protecting enamel.
5. Remineralizing Paste: Products like MI Paste that contain calcium phosphate to rebuild enamel.
How does aging affect enamel on teeth?
Aging affects enamel by causing it to wear down due to factors like decreased mineral content and increased exposure to acids from food and beverages. This can lead to enamel thinning, making teeth more susceptible to decay, sensitivity, and discoloration. Additionally, older adults may produce less saliva, which is essential for remineralizing enamel and protecting against cavities.
What treatments are available for damaged enamel?
Treatments for damaged enamel include:
1. Fluoride Treatments: Professional fluoride applications can help remineralize enamel.
2. Dental Sealants: Thin plastic coatings applied to teeth to protect enamel.
3. Bonding: Composite resin applied to damaged areas to restore appearance and function.
4. Crowns: Caps placed over severely damaged teeth for protection and strength.
5. Veneers: Thin shells bonded to the front of teeth to improve aesthetics and cover damage.
6. Desensitizing Toothpaste: Helps reduce sensitivity caused by enamel erosion.
Consult a dentist for the best treatment tailored to individual needs.
How does enamel thickness vary among individuals?

Enamel thickness varies among individuals due to genetic factors, age, dietary habits, and oral health. Generally, enamel is thicker in molars than in incisors. It can also be influenced by environmental factors such as fluoride exposure and overall dental hygiene practices.
What is the relationship between enamel and teeth sensitivity?
Enamel protects teeth from sensitivity by acting as a barrier against external stimuli. When enamel wears down or is damaged, it exposes the underlying dentin, which contains nerve endings. This exposure can lead to increased sensitivity to temperature changes, sweet or acidic foods, and pressure. Maintaining healthy enamel is crucial for preventing teeth sensitivity.
Conclusion about # What Is the Role of Enamel in Teeth Anatomy?
In summary, enamel plays a critical role in teeth anatomy by serving as the protective outer layer that shields against decay and damage. Its unique properties differentiate it from other dental layers, and its health can be influenced by various factors including diet, aging, and fluoride exposure. While enamel cannot regenerate on its own, proactive measures such as using specific dental products can help strengthen and protect it. Understanding these aspects is essential for maintaining overall dental health. For further insights and assistance on enamel and dental care, you can rely on Tooth1.