Did you know that your teeth have a built-in "emergency room" called dental pulp? This soft tissue, located in the center of each tooth, plays a crucial role in maintaining tooth health. In this article, we delve into the significance of dental pulp, exploring its functions, its contribution to tooth sensitivity, and the consequences of damage. We’ll discuss common causes of pulp damage, symptoms of pulp infection, and the intricacies of root canal treatment. Additionally, we’ll touch on how age impacts pulp health, preventive measures to protect it, and the latest advancements in pulp management. Join us as we uncover the vital role of dental pulp in overall dental health with insights from Tooth1.
What is dental pulp and where is it located in teeth?
Dental pulp is the soft tissue inside a tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. It is located in the center of the tooth, within the pulp chamber, and extends down through the root canals. The pulp plays a crucial role in tooth health, providing nourishment and sensory functions.
Why is pulp vital for tooth health?
Pulp is vital for tooth health because it contains nerves and blood vessels that nourish the tooth and maintain its vitality. It plays a crucial role in sensing temperature and pressure, helping protect against injury. Additionally, pulp facilitates the formation of dentin, the hard tissue surrounding it, which is essential for the tooth's structure and strength. Without healthy pulp, teeth can become brittle, prone to decay, and susceptible to infection.
What are the main functions of dental pulp?
The main functions of dental pulp are:
1. Nourishment: Supplies essential nutrients to the tooth through blood vessels.
2. Sensation: Contains nerve endings that provide sensitivity to temperature and pain.
3. Formation: Responsible for the development and maintenance of the tooth structure, including dentin production.
4. Defense: Helps protect against infection and trauma by initiating immune responses.
How does pulp contribute to tooth sensitivity?
Pulp is the innermost soft tissue of a tooth, containing nerves and blood vessels. It contributes to tooth sensitivity by transmitting sensations, such as pain and temperature changes, to the brain. When the pulp is exposed due to decay, cracks, or gum recession, it can lead to heightened sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli. Inflammation or infection of the pulp, known as pulpitis, further exacerbates sensitivity, causing discomfort and pain.
What happens when the pulp is damaged?
When the pulp is damaged, it can lead to inflammation, infection, and pain. This may result in pulpitis, which can cause severe toothaches. If left untreated, it can progress to an abscess, leading to further complications and the potential loss of the tooth.
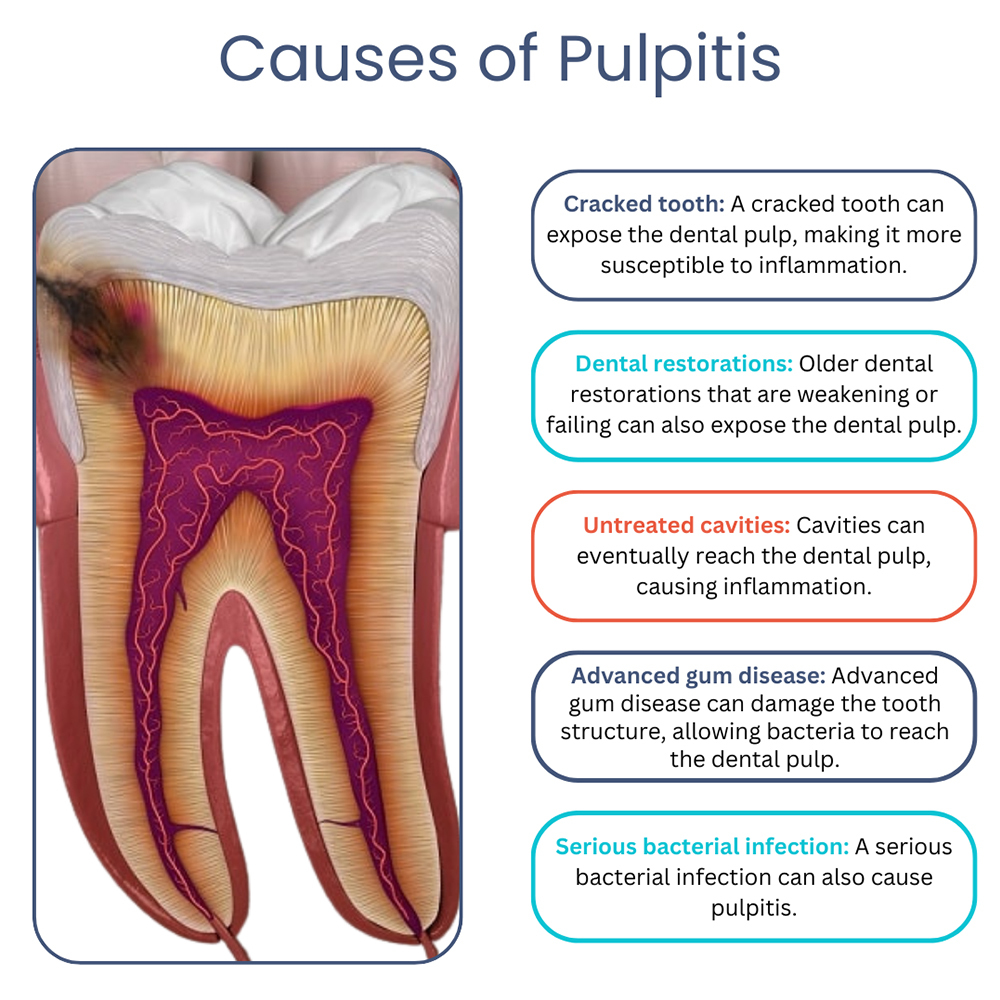
What are the common causes of pulp damage?
Common causes of pulp damage include:
1. Cavities: Bacterial infection from untreated tooth decay can reach the pulp.
2. Trauma: Physical injury to the tooth can lead to pulp exposure or damage.
3. Cracks or Fractures: Cracked teeth can allow bacteria to enter and harm the pulp.
4. Dental Procedures: Some treatments, like drilling for fillings, can inadvertently damage the pulp.
5. Gum Disease: Advanced gum disease can lead to pulp inflammation.
6. Extreme Temperature Changes: Exposure to hot or cold substances can trigger pulp irritation.
How can pulpitis affect overall dental health?
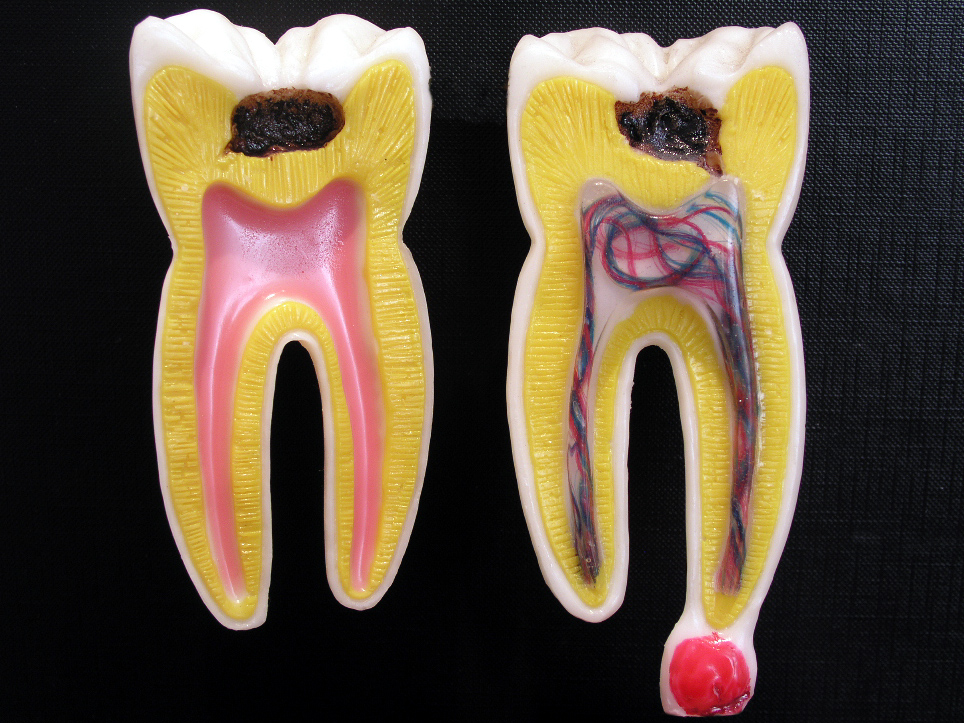
Pulpitis can significantly impact overall dental health by causing inflammation of the dental pulp, leading to pain, infection, and potential tooth loss. If untreated, it can result in abscess formation, affecting surrounding teeth and jawbone health. Chronic pulpitis may also contribute to systemic health issues, as oral infections can spread to other parts of the body. Regular dental check-ups are essential to address pulpitis early and maintain optimal dental health.
What are the symptoms of pulp infection?
Symptoms of pulp infection include:
1. Severe toothache or pain that may be sharp, throbbing, or persistent.
2. Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, even after the stimulus is removed.
3. Swelling and tenderness in the gums around the affected tooth.
4. Discoloration of the tooth, often appearing darker.
5. Bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth.
6. Pus or discharge from the affected area.
7. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw.
If you experience these symptoms, consult a dentist promptly.
How is dental pulp treated during a root canal?
During a root canal, the dental pulp is treated by first numbing the area with local anesthesia. The dentist then creates an opening in the tooth to access the pulp chamber. The infected or damaged pulp is removed using specialized tools. After cleaning and disinfecting the pulp chamber and root canals, the space is filled with a biocompatible material called gutta-percha. Finally, the tooth is sealed and may be restored with a crown to ensure its function and strength.
What is the role of pulp in tooth development?
The pulp is the soft tissue inside a tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. It plays a crucial role in tooth development by supplying nutrients and moisture to the tooth, facilitating root formation and growth. Additionally, the pulp helps in sensory functions, allowing the tooth to respond to temperature and pressure changes.
Can dental pulp regenerate after injury?
No, dental pulp cannot fully regenerate after injury. However, it can heal to some extent through a process called reparative dentin formation, but this is limited and may not restore the pulp to its original state.
## How Do Donkey Teeth Develop and What Role Does Pulp Play?
The pulp is the innermost part of the tooth, containing nerves and blood vessels. Its importance lies in providing nourishment to the tooth, facilitating sensation, and maintaining the health of surrounding tissues.
Learn more about donkey teeth
What are the differences between vital and non-vital pulp?
Vital pulp contains live nerve endings and blood vessels, providing sensation and nourishment to the tooth. Non-vital pulp, on the other hand, is necrotic and lacks blood supply, often resulting from injury or infection. Vital pulp is healthy and responsive, while non-vital pulp indicates a compromised tooth requiring treatment.
How does age affect the health of dental pulp?
Age affects the health of dental pulp in several ways. As individuals age, the pulp chamber typically decreases in size due to secondary dentin formation, which can lead to reduced pulp vitality. Older adults may experience decreased blood supply and nerve sensitivity within the pulp, making it less responsive to infection or trauma. Additionally, age-related conditions, such as increased incidence of caries and periodontal disease, can compromise the pulp's health, leading to a higher risk of pulpitis or necrosis.
What preventive measures can protect dental pulp?
Preventive measures to protect dental pulp include:
1. Regular Dental Check-ups: Routine visits allow for early detection of issues.
2. Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice daily and flossing prevents decay.
3. Fluoride Treatments: Strengthens enamel, reducing the risk of cavities.
4. Diet Management: Limiting sugary foods and drinks helps prevent tooth decay.
5. Sealants: Dental sealants can protect the grooves of molars from decay.
6. Avoiding Tobacco: Reduces the risk of gum disease, which can affect pulp health.
7. Wearing Mouthguards: Protects against injury during sports or teeth grinding.
How does pulp health relate to gum disease?
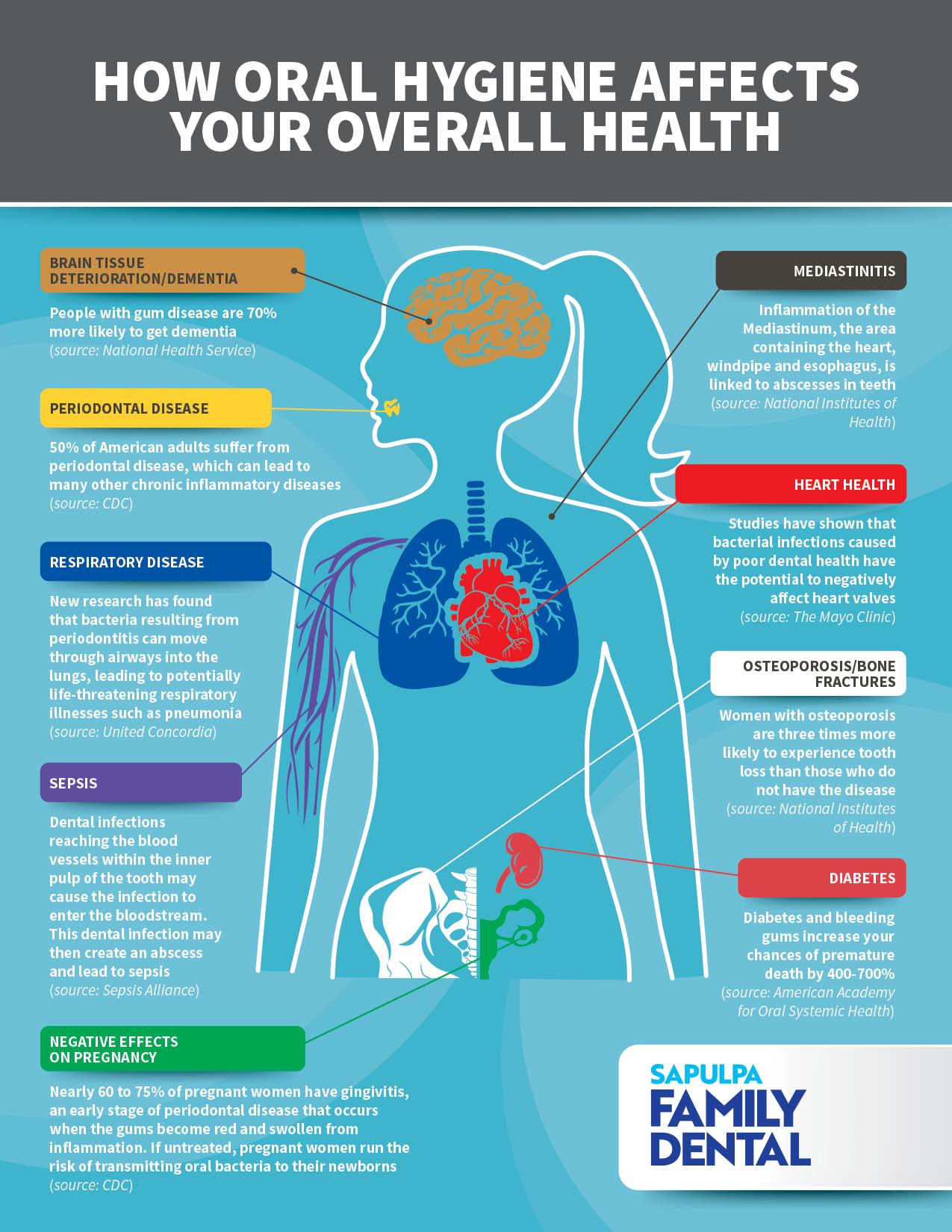
Pulp health is directly related to gum disease because inflammation or infection in the gums can extend to the pulp. Healthy gums support the teeth and help prevent bacteria from entering the pulp. If gum disease progresses, it can lead to pulpitis, which is inflammation of the pulp, potentially resulting in toothache or abscess. Maintaining gum health is essential to protect the pulp and overall oral health.
What advancements are there in pulp treatment and management?
Advancements in pulp treatment and management include:
1. Regenerative Endodontics: Techniques that promote the healing and regeneration of pulp tissue using biomaterials and stem cells.
2. Cone Beam CT Imaging: Enhanced imaging technology for precise diagnosis and treatment planning of pulp-related issues.
3. Bioceramic Materials: Use of biocompatible materials for pulp capping and sealing, improving the success rates of treatments.
4. Minimally Invasive Techniques: Development of less invasive procedures to preserve more tooth structure during treatment.
5. Laser Therapy: Utilization of lasers for disinfecting root canals and reducing treatment time while minimizing discomfort.
6. Pulp Preservation Methods: Strategies to maintain pulp vitality in cases of trauma or deep caries, focusing on early intervention.
These advancements aim to improve outcomes, reduce pain, and enhance patient comfort in pulp treatment.
Conclusion about # What Is the Pulp and Its Importance in Teeth?
In summary, understanding dental pulp is crucial for maintaining overall tooth health. This vital tissue not only supports tooth development and sensitivity but also plays a significant role in protecting against infections. Damage to the pulp can lead to serious complications like pulpitis, impacting overall dental health. Preventive measures, such as regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene, are essential for safeguarding pulp health. For comprehensive insights and support regarding dental pulp and other aspects of oral care, Tooth1 is here to help.
