Did you know that humans have a set of teeth designed to handle everything from crunching carrots to tearing steak, much like a Swiss Army knife? In this article, we explore the various types of teeth—incisors, canines, premolars, and molars—and their essential roles in digestion. We'll dive into how each type contributes to breaking down food, the impact of dental health on digestive efficiency, and the consequences of missing or misaligned teeth. Additionally, we’ll discuss the influence of diet, oral bacteria, and dental care on overall digestive health. Discover how understanding your teeth can lead to better digestion and health with insights from Tooth1.
What are the different types of teeth in humans?
Humans have four types of teeth:
1. Incisors: Sharp, flat teeth at the front used for cutting food.
2. Canines: Pointed teeth next to incisors for tearing food.
3. Premolars: Flat-topped teeth behind canines for crushing and grinding food.
4. Molars: Larger, flat teeth at the back for grinding and chewing food.
Each type plays a specific role in the digestion process.
How do incisors contribute to the digestive process?
Incisors contribute to the digestive process by cutting and slicing food into smaller pieces. Their sharp, flat edges allow for efficient biting, making it easier to chew and mix food with saliva, which begins the breakdown of carbohydrates. This initial mechanical digestion is crucial for facilitating further digestion in the stomach and intestines.
What is the role of canines in chewing food?
Canines play a crucial role in chewing food by tearing and gripping. Their pointed shape helps break down tougher food items, facilitating easier swallowing and digestion. This action complements the grinding function of molars, ensuring effective food processing in the mouth.
How do premolars aid in digestion?
Premolars aid in digestion by grinding and crushing food, breaking it down into smaller pieces to facilitate easier swallowing and digestion. Their flat surfaces with ridges are designed for this purpose, helping to prepare food for the further processing that occurs in the stomach and intestines.
What functions do molars serve in the digestive system?
Molars are responsible for grinding and crushing food during chewing, aiding in the mechanical breakdown of food to facilitate digestion. They have a broad, flat surface designed for this purpose and play a crucial role in mixing food with saliva, which begins the digestive process. Additionally, molars help in the overall efficiency of swallowing and processing food in the digestive system.
How do teeth wear and tear affect digestion?
Teeth wear and tear negatively affect digestion by impairing the ability to chew food properly. Damaged or worn teeth can lead to difficulty breaking down food into smaller pieces, which hinders the digestive process. This can result in larger food particles entering the stomach, making it harder for enzymes to digest them effectively. Additionally, poor chewing increases the risk of digestive issues like indigestion or bloating. Maintaining healthy teeth is crucial for efficient digestion.
What is the importance of dental health for proper digestion?
Dental health is crucial for proper digestion because teeth break down food into smaller pieces, making it easier for enzymes to digest it. Healthy teeth ensure effective chewing, which initiates the digestive process. Damaged or missing teeth can lead to inadequate food breakdown, causing digestive issues and poor nutrient absorption. Overall, maintaining dental health supports efficient digestion and overall well-being.
How do wisdom teeth impact the digestive process?
Wisdom teeth impact the digestive process primarily through their role in chewing. They help break down food into smaller pieces, aiding in digestion. If wisdom teeth are misaligned or impacted, they can cause pain, leading to reduced chewing efficiency. This can result in larger food particles entering the digestive system, making it harder for subsequent digestive processes to break down food effectively. Additionally, issues with wisdom teeth may lead to infections, which can further complicate digestion by causing discomfort or preventing adequate food intake.
What happens when teeth are missing in relation to digestion?

Missing teeth can impair digestion by reducing the efficiency of food breakdown. Chewing is less effective, leading to larger food particles entering the digestive tract. This can hinder the stomach and intestines' ability to process food, potentially causing digestive issues such as bloating, gas, or discomfort. Additionally, inadequate chewing may affect nutrient absorption, as properly chewed food is essential for optimal digestion.
How does tooth alignment influence digestion?
Tooth alignment affects digestion by influencing how effectively food is broken down during chewing. Properly aligned teeth facilitate efficient biting and grinding, leading to smaller food particles that are easier to digest. Misaligned teeth can cause uneven wear, discomfort, and difficulty in chewing, which may result in larger food pieces entering the digestive system. This can hinder digestion and lead to gastrointestinal issues.
What are common dental issues that can affect digestion?
Common dental issues that can affect digestion include:
1. Tooth Decay: Cavities can lead to pain while chewing, impacting food intake and digestion.
2. Gum Disease: Inflammation and infection in the gums can cause discomfort and affect eating habits.
3. Missing Teeth: Gaps can hinder proper chewing, leading to larger food pieces that are harder to digest.
4. Misalignment: Crooked teeth can interfere with the bite, making chewing inefficient.
5. Tooth Sensitivity: Pain from hot or cold foods can deter individuals from consuming a balanced diet.
6. Oral Infections: Infections can cause swelling and pain, impacting the ability to eat comfortably.
## How Do Different Types of Donkey Teeth Affect Their Digestion?
Donkeys typically have 36 to 44 teeth, depending on their age and sex. Their teeth are adapted for grinding tough vegetation, playing a crucial role in digestion by breaking down food for better nutrient absorption.
Learn more about donkey teeth
How does diet impact the health of different types of teeth?
Diet impacts the health of different types of teeth through their specific functions and the types of food they encounter.
1. Incisors: These sharp, flat teeth are designed for cutting food. A diet high in sugars can lead to decay, affecting their cutting ability.
2. Canines: Pointed canines help tear food. A lack of tough foods can weaken them, leading to issues with tearing.
3. Premolars: These teeth grind food. A diet lacking in fibrous foods can result in plaque buildup, impacting their grinding efficiency.
4. Molars: Molars are crucial for crushing and grinding. A diet high in acidic foods can erode enamel, reducing their effectiveness in digestion.
Overall, a balanced diet rich in nutrients supports the health of all tooth types, preventing decay and maintaining their functionality in the digestive process.
What is the connection between oral bacteria and digestion?
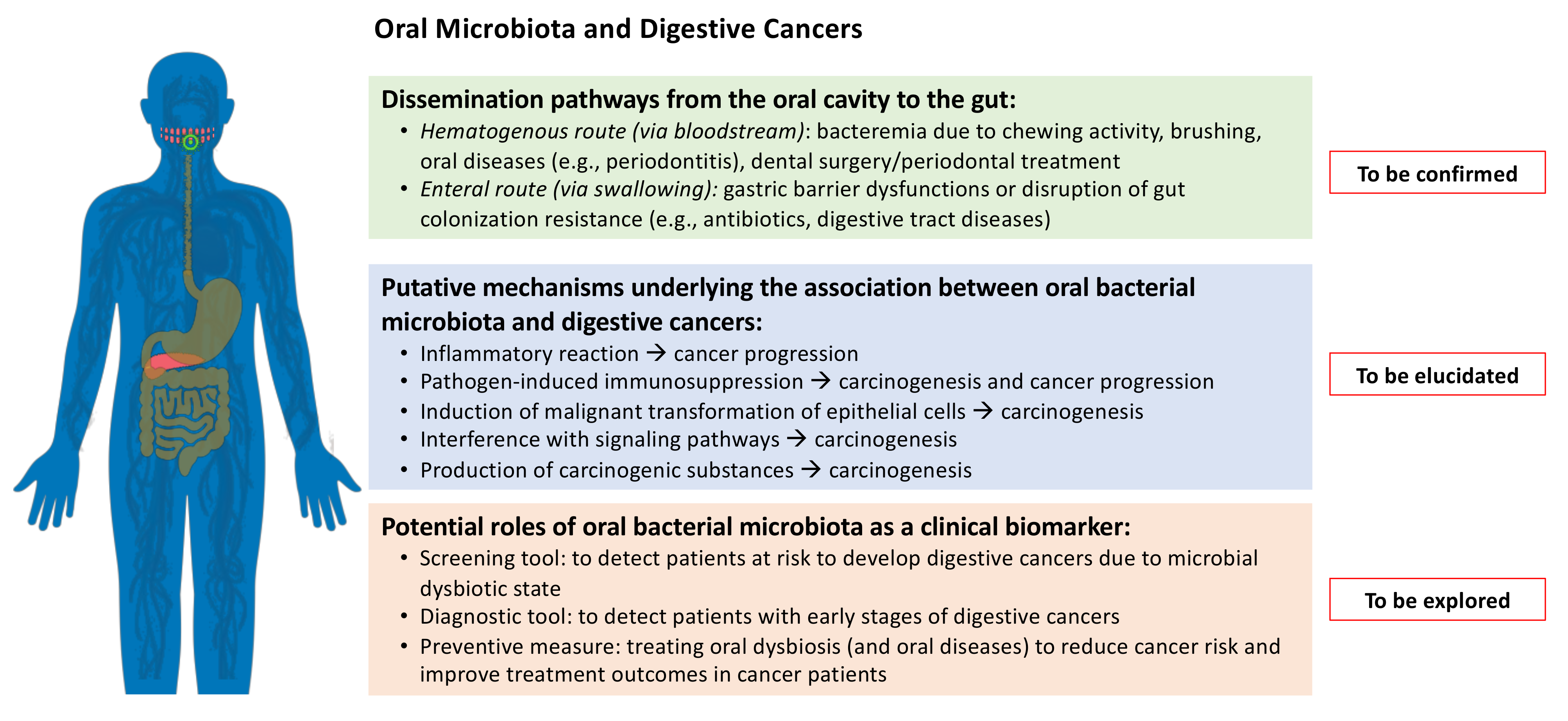
Oral bacteria play a crucial role in digestion by breaking down food particles and aiding in the initial stages of digestion. Specific bacteria help ferment carbohydrates, producing short-chain fatty acids that can be absorbed by the body. Additionally, a healthy balance of oral bacteria contributes to the overall health of the digestive system, influencing gut microbiota and enhancing nutrient absorption.
How can dental care improve digestive health?
Dental care improves digestive health by ensuring proper chewing and breakdown of food, which aids digestion. Healthy teeth facilitate the mechanical processing of food, allowing enzymes in saliva to start digestion. Additionally, good oral hygiene prevents infections that can disrupt digestive processes, such as gum disease, which may lead to systemic inflammation affecting gut health. Maintaining regular dental check-ups ensures optimal tooth function and overall digestive efficiency.
What are the stages of digestion that involve teeth?
The stages of digestion that involve teeth are:
1. Mastication: The process of chewing food, where teeth break down food into smaller pieces.
2. Mixing with Saliva: While chewing, teeth help mix food with saliva, which begins the digestion of carbohydrates.
3. Forming a Bolus: Teeth assist in shaping the chewed food into a soft mass (bolus) for easier swallowing.
These stages are essential for effective digestion.
How do children’s teeth differ in function from adult teeth?
Children's teeth, known as primary or deciduous teeth, differ from adult teeth in that they are smaller, have thinner enamel, and are designed to aid in the transition to solid foods and speech development. They typically have fewer roots and are more spaced out to accommodate the growth of adult teeth. Functionally, primary teeth help with chewing, maintaining space for permanent teeth, and guiding their emergence. Adult teeth, or permanent teeth, are larger, stronger, and designed for long-term use, with more complex root structures for stability and durability in chewing a wider variety of foods.
Conclusion about # Teeth Types and Their Role in Digestion
Understanding the various types of teeth and their specific roles in digestion is crucial for maintaining overall health. Each tooth type—incisors, canines, premolars, and molars—contributes uniquely to the digestive process. Proper dental care is essential to prevent issues that could impair digestion, such as tooth wear, misalignment, and decay. Ensuring good oral hygiene not only preserves your teeth but also enhances your digestive efficiency. For more detailed insights and guidance on dental health's impact on digestion, refer to Tooth1.

