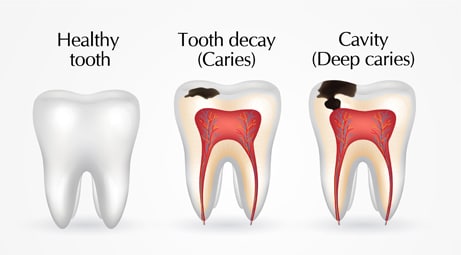
What are teeth caries and how do they develop?
Related Topic

Further details are currently unavailable. learn more here Do You Need a Root Canal? When a Cavity Becomes Serious Source Source
Teeth caries, also known as tooth decay or cavities, are areas of damage on the hard surface of teeth caused by bacterial infection. They develop when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode tooth enamel, often due to poor oral hygiene, frequent sugar consumption, and inadequate fluoride. As the enamel breaks down, the decay progresses to deeper layers of the tooth, potentially leading to pain, infection, and tooth loss if untreated.
What are the common signs of teeth caries?
Common signs of teeth caries include:
1. Tooth Sensitivity: Pain or discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods.
2. Visible Holes or Pits: Dark spots or holes in the teeth.
3. Toothache: Persistent pain in or around the affected tooth.
4. Discoloration: Brown, black, or white stains on the tooth surface.
5. Bad Breath: Persistent foul odor from the mouth.
6. Swelling: Swelling of the gums around the affected tooth.
If you notice any of these signs, consult a dentist for evaluation and treatment.
How can I prevent teeth caries effectively?

To prevent teeth caries effectively:
1. Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
2. Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth.
3. Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
4. Rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash.
5. Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
6. Drink plenty of water, especially fluoridated water.
7. Consider dental sealants for added protection.
What treatments are available for teeth caries?
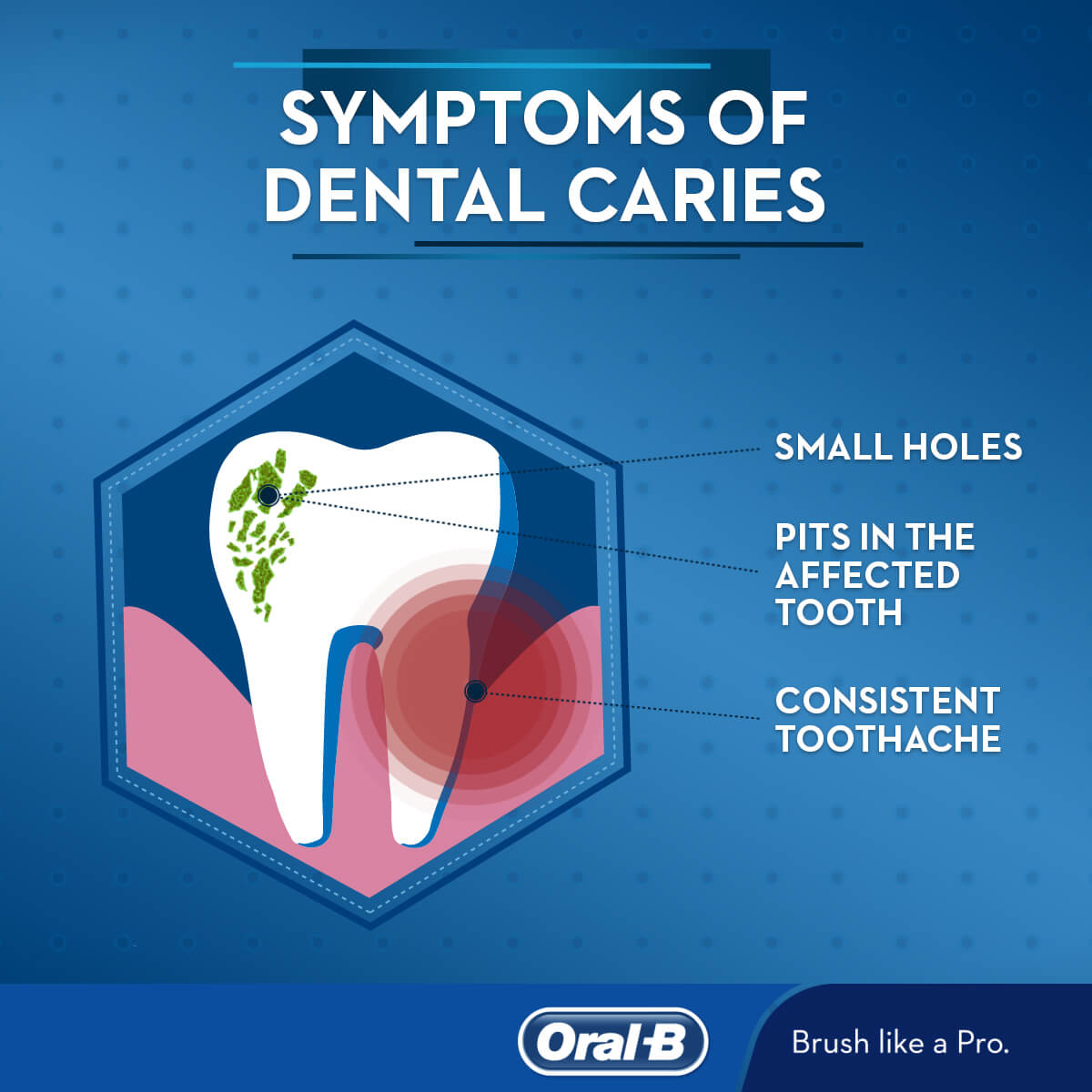
Treatments for teeth caries include:
1. Fluoride Treatments: Professional fluoride applications to help remineralize early decay.
2. Dental Sealants: Protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth to prevent decay.
3. Fillings: Removal of decayed material followed by filling the cavity with materials like composite resin, amalgam, or gold.
4. Crowns: Caps placed over a tooth to restore its shape and function, used for extensive decay.
5. Root Canals: Treatment for decay that has reached the tooth’s pulp, involving cleaning and sealing the inside of the tooth.
6. Tooth Extractions: Removal of the tooth if it is severely damaged and cannot be restored.
Can teeth caries be reversed in early stages?
Yes, teeth caries can be reversed in the early stages. Remineralization can occur through good oral hygiene, fluoride treatments, and a diet low in sugars. Regular dental check-ups are also essential for monitoring and managing early caries.
How does diet impact the development of teeth caries?
Diet significantly impacts the development of tooth caries. High sugar consumption feeds harmful bacteria in the mouth, leading to acid production that erodes enamel. Frequent snacking on sugary or acidic foods increases the risk of decay. A diet lacking in essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus can weaken teeth, making them more susceptible to caries. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, dairy, and whole grains supports oral health and helps prevent cavities.
What role does fluoride play in preventing teeth caries?
Fluoride helps prevent teeth caries by strengthening tooth enamel, making it more resistant to acid attacks from plaque bacteria and sugars. It promotes the remineralization of early decay and inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth. Regular exposure to fluoride, through toothpaste or water, significantly reduces the risk of cavities.
How often should I visit the dentist to check for teeth caries?
You should visit the dentist at least twice a year for regular check-ups to check for teeth caries. If you’re at higher risk for cavities, your dentist may recommend more frequent visits.
What are the long-term effects of untreated teeth caries?
Untreated teeth caries can lead to several long-term effects, including:
1. Tooth Decay: Continued deterioration of the tooth structure, leading to cavities.
2. Tooth Loss: Severe decay can result in the need for extraction due to structural damage.
3. Infection: Bacteria can enter the tooth, causing abscesses and systemic infections.
4. Pain and Discomfort: Chronic pain and sensitivity can develop, affecting quality of life.
5. Gum Disease: Caries can contribute to periodontal issues, resulting in gum inflammation and recession.
6. Affects on Nutrition: Pain may lead to difficulty eating, impacting overall nutrition.
7. Increased Treatment Costs: Delaying treatment often results in more extensive and costly dental procedures later on.
Prompt treatment of teeth caries is essential to prevent these complications.
Are children more susceptible to teeth caries?
Yes, children are more susceptible to teeth caries due to factors like developing dental hygiene habits, higher sugar intake, and weaker enamel compared to adults.
How do teeth caries differ from other dental issues?
Teeth caries, or dental cavities, are specific areas of decay caused by bacteria that produce acids from sugars, leading to demineralization of tooth enamel. Unlike other dental issues such as gum disease, which affects the supporting structures of teeth, or tooth sensitivity, which involves nerve reactions, caries directly damage tooth structure. Caries can progress through stages, starting from initial demineralization to potential tooth loss if untreated, whereas other issues may not involve structural damage. Additionally, caries require restorative treatments like fillings, while gum disease may need periodontal treatment.
What natural remedies can help with teeth caries?
Natural remedies that may help with teeth caries include:
1. Fluoride Treatments: Use fluoride toothpaste or mouth rinses to strengthen enamel.
2. Oil Pulling: Swish coconut or sesame oil in your mouth for 10-15 minutes to reduce bacteria.
3. Clove Oil: Apply clove oil for its antibacterial properties and to relieve tooth pain.
4. Salt Water Rinse: Rinse with salt water to reduce inflammation and bacteria.
5. Green Tea: Drink green tea for its antioxidants that may help inhibit cavity-causing bacteria.
6. Xylitol: Chew xylitol gum to reduce cavity-causing bacteria and stimulate saliva production.
7. Turmeric: Use turmeric paste for its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
8. Homemade Toothpaste: Combine baking soda and coconut oil for a natural cleaning paste.
Consult a dentist for a comprehensive treatment plan.
How can I identify teeth caries at home?
To identify teeth caries at home, look for the following signs:
1. Discoloration: Check for dark spots or white patches on the teeth.
2. Sensitivity: Notice if you experience pain or discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods.
3. Visible Holes: Inspect for any visible cavities or holes in the teeth.
4. Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath can indicate decay.
5. Pain: Pay attention to any toothaches or persistent pain in specific areas.
If you notice any of these signs, consider visiting a dentist for a thorough examination.
What is the connection between teeth caries and gum disease?
Teeth caries and gum disease are interconnected oral health issues. Caries, caused by bacteria that produce acids leading to tooth decay, can contribute to gum disease by creating pockets for bacteria to thrive. Inflammation from caries can also weaken the gums, making them more susceptible to infection. Conversely, gum disease can worsen caries by allowing bacteria to invade deeper into tooth structures. Managing both conditions is essential for overall oral health.
How does oral hygiene affect the risk of teeth caries?
Oral hygiene significantly reduces the risk of teeth caries by minimizing plaque buildup and harmful bacteria. Regular brushing and flossing remove food particles and prevent the formation of acids that erode enamel. Good oral hygiene practices, such as using fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash, strengthen enamel and help remineralize early carious lesions. Neglecting oral hygiene increases plaque accumulation, leading to higher acid production and greater susceptibility to cavities.
What should I do if I suspect I have teeth caries?
If you suspect you have teeth caries, schedule an appointment with a dentist as soon as possible for an evaluation. Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice daily and flossing. Avoid sugary foods and drinks to prevent further decay. If pain or sensitivity occurs, inform your dentist during your visit.