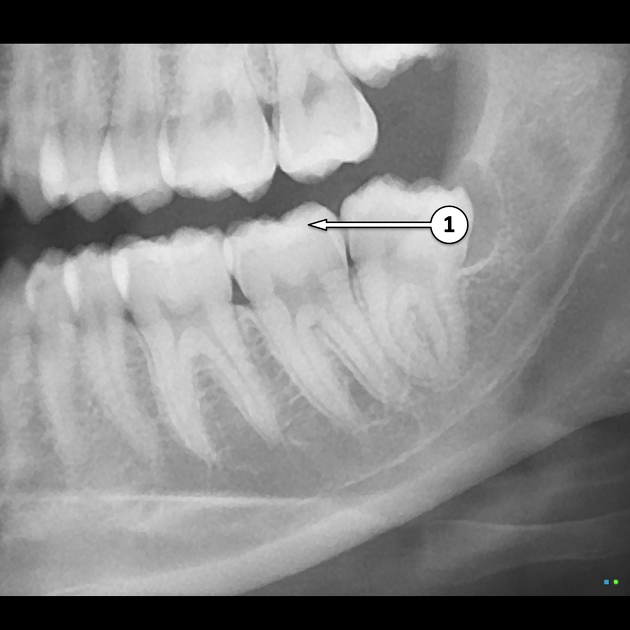
Did you know that teeth are like icebergs—most of their structure is hidden beneath the surface? Understanding tooth anatomy is crucial for interpreting dental X-rays, which reveal not just the visible parts of teeth but also their inner workings. This article dives into the basic structure of a tooth, how dental X-rays visualize these components, and the various types of X-rays used in diagnosis. We’ll discuss the critical role of enamel, how X-rays detect decay and gum disease, and their importance in orthodontics and planning extractions. Finally, we’ll cover safety precautions during X-ray procedures. Discover how Tooth1 can help you navigate these essential aspects of dental health!
What is the basic structure of a tooth?
The basic structure of a tooth includes:
1. Enamel: The hard, outer layer that protects the tooth.
2. Dentin: The layer beneath enamel, softer than enamel, providing support.
3. Pulp: The innermost part containing nerves and blood vessels.
4. Cementum: A layer covering the tooth root, helping anchor it to the jawbone.
5. Periodontal Ligament: Tissue connecting the tooth to the surrounding bone, providing support and shock absorption.
How do dental X-rays visualize tooth anatomy?
Dental X-rays visualize tooth anatomy by using radiation to create images of the teeth, bones, and surrounding tissues. The X-rays penetrate soft tissue but are absorbed by dense structures like teeth and bone, producing contrasting images. These images reveal details such as the shape, position, and condition of teeth, roots, and surrounding bone, enabling dentists to diagnose issues like cavities, infections, and bone loss.
What types of dental X-rays are used to examine teeth?
The main types of dental X-rays used to examine teeth include:
1. Bitewing X-rays: Show upper and lower teeth in one area, useful for detecting cavities.
2. Periapical X-rays: Focus on one or two teeth, capturing the entire tooth and surrounding bone.
3. Panoramic X-rays: Provide a broad view of the entire mouth, showing all teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures.
4. Cone Beam CT (CBCT): Offers 3D images for detailed examination of dental structures, especially for implants and complex cases.
How do X-rays reveal tooth decay and cavities?
X-rays reveal tooth decay and cavities by using electromagnetic radiation to create images of the teeth and surrounding structures. When X-rays pass through the mouth, healthy tooth enamel appears white, while areas affected by decay absorb more radiation and appear darker on the X-ray image. This contrast allows dentists to identify cavities and assess the extent of tooth decay, helping in diagnosis and treatment planning.
What is the role of enamel in tooth X-rays?
Enamel plays a crucial role in tooth X-rays as it is the outermost layer of the tooth and appears radiopaque, meaning it blocks X-rays and appears white on the film. This allows dentists to assess the integrity of the tooth structure, identify cavities, and evaluate the overall dental health by providing clear images of the enamel's condition.
How can dental X-rays show tooth roots and their structures?
Dental X-rays show tooth roots and their structures by using radiation to create images of the internal anatomy of teeth and surrounding bone. The X-rays penetrate soft tissue but are absorbed by denser materials like bone and tooth enamel, resulting in a clear contrast on the film or digital image. This allows dentists to visualize the roots, periodontal ligaments, and surrounding bone structures, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Why is understanding tooth anatomy important for X-ray interpretation?
Understanding tooth anatomy is crucial for X-ray interpretation because it helps identify the specific structures and conditions of teeth, such as decay, fractures, and periodontal disease. Knowledge of anatomy allows for accurate assessment of X-ray images, ensuring proper diagnosis and treatment planning. Recognizing the spatial relationships between different tooth structures aids in distinguishing normal variations from pathological changes, ultimately improving patient care.
How do X-rays help in diagnosing gum disease related to teeth?
X-rays help diagnose gum disease by revealing bone loss around teeth, detecting periodontal pockets, and identifying changes in the bone structure. They show the extent of infection and help assess the health of supporting tissues. This imaging aids dentists in planning appropriate treatments for gum disease.
What are the differences between bitewing and periapical X-rays?
Bitewing X-rays capture the upper and lower teeth in one area of the mouth, focusing on the crowns and interproximal areas, useful for detecting cavities between teeth. Periapical X-rays show the entire tooth, from crown to root, and surrounding bone, ideal for assessing issues like infections or bone loss.
How do dental X-rays assist in planning tooth extractions?
Dental X-rays assist in planning tooth extractions by providing detailed images of tooth anatomy, surrounding bone structure, and potential complications. They help identify the position of the tooth roots, assess the health of adjacent teeth, and reveal any underlying issues such as infections or cysts. This information enables dentists to devise a precise extraction plan, ensuring a safer and more effective procedure.
What information do X-rays provide about tooth alignment and occlusion?
X-rays provide critical information about tooth alignment and occlusion by revealing the positioning of teeth relative to one another and the jaw. They help identify misalignments, such as crowding or spacing issues, and assess how upper and lower teeth fit together when biting or chewing. Additionally, X-rays can show the relationship of teeth to surrounding bone structures, aiding in diagnosing potential orthodontic concerns or occlusal discrepancies.
## How Do Donkey Teeth Anatomy and Dental X-Rays Work Together?

Tooth anatomy is crucial for interpreting dental X-rays because it helps identify the structure, position, and health of teeth, including roots and surrounding bone. Accurate knowledge of tooth anatomy allows dentists to diagnose issues like cavities, fractures, and periodontal disease effectively.
Learn more about donkey teeth
How can X-rays detect issues with dental fillings and crowns?
X-rays can detect issues with dental fillings and crowns by revealing underlying problems not visible to the naked eye. They show the condition of the tooth structure beneath the restoration, identify decay around the filling or crown, and assess the fit and integrity of the restoration. Additionally, X-rays can help diagnose any potential infections or issues with the surrounding bone.
What is the significance of dental X-rays in orthodontics?
Dental X-rays are crucial in orthodontics as they provide detailed images of tooth anatomy, root structure, and jaw alignment. They help orthodontists assess the position of teeth, identify potential issues like impactions or misalignments, and plan effective treatment strategies. X-rays also allow for monitoring changes over time, ensuring that the orthodontic treatment progresses as intended.
How do dental X-rays contribute to understanding tooth development?
Dental X-rays provide critical insights into tooth development by allowing dentists to visualize the position, structure, and health of teeth beneath the surface. They reveal the stages of tooth eruption, identify abnormalities like impaction or misalignment, and assess the formation of roots and surrounding bone. This information aids in diagnosing issues early, planning treatments, and monitoring growth over time.
What precautions should be taken during dental X-ray procedures?
During dental X-ray procedures, precautions include:
1. Lead Aprons: Use lead aprons and collars to protect other parts of the body from radiation.
2. Minimize Exposure: Limit the number of X-rays and only take them when necessary.
3. Proper Positioning: Ensure correct positioning of the X-ray machine and the patient to avoid retakes.
4. Use of Digital X-rays: Prefer digital X-rays for lower radiation exposure and better image quality.
5. Patient History: Review patient history for prior X-rays and concerns about radiation sensitivity.
6. Shielding: Use additional shielding for vulnerable areas when applicable.
7. Operator Training: Ensure that the operator is trained in proper X-ray techniques and safety protocols.
How do X-rays help in identifying impacted teeth?
X-rays help identify impacted teeth by providing a clear image of the tooth's position relative to surrounding structures. They reveal the location of the tooth within the jaw, any obstruction from adjacent teeth, and the degree of impaction. This information is crucial for planning treatment, such as extraction or orthodontic intervention.
Conclusion about # How Does Tooth Anatomy Relate to Dental X-Rays?
Understanding tooth anatomy is essential for effective dental care, particularly when interpreting dental X-rays. These imaging tools not only reveal critical details about tooth structure, including roots, enamel, and potential decay, but they also aid in diagnosing conditions such as gum disease and impacted teeth. By utilizing various types of X-rays, dental professionals can identify issues with fillings, plan extractions, and assess overall tooth alignment. Knowledge of tooth anatomy enhances the accuracy of these diagnoses, ultimately leading to better treatment outcomes. For comprehensive insights and assistance regarding teeth, consider exploring the resources offered by Tooth1.