Did you know that a dog’s bite can exert up to 450 pounds of pressure per square inch? In this article, we dive into the world of canine teeth, exploring why dogs have sharp teeth, their purpose, and how they differ from human teeth. We’ll cover the types of teeth dogs possess, the risks associated with dog bites, and essential dental care tips to keep your furry friend’s mouth healthy. Additionally, we’ll discuss the development of puppy teeth, signs of dental issues, and how to train dogs to avoid biting. Join us as we uncover the fascinating anatomy of dog teeth and the importance of proper dental hygiene, all brought to you by Tooth1.
Why Do Dogs Have Sharp Teeth?
Dogs have sharp teeth primarily for two reasons: to effectively grasp and tear meat, as they are carnivorous by nature, and to aid in their survival skills like hunting and defense. Their canine teeth are designed for puncturing, while their premolars and molars are used for grinding food.
What Purpose Do Canine Teeth Serve?
Canine teeth serve multiple purposes:
1. Tearing Food: They are designed for tearing and gripping, helping to process meat and other tough foods.
2. Defense: Canine teeth can be used as weapons for defense against threats.
3. Aesthetic Function: In many species, including humans, they contribute to the overall appearance and expression of the mouth.
Overall, canine teeth are crucial for feeding, protection, and social signaling.
## How Do Donkey Canines Differ from Their Other Teeth?
Donkey teeth include incisors and molars, but their canines are less pronounced. Canines in donkeys are small and not as sharp as in other animals, serving primarily for chewing rather than tearing.
Learn more about donkey teeth
How Do Dog Teeth Differ from Human Teeth?
Dog teeth differ from human teeth in several key ways:
1. Shape and Size: Dog teeth are generally sharper and more pointed, designed for tearing and chewing meat, while human teeth are flatter, adapted for grinding a variety of food.
2. Number: Dogs have 42 teeth, whereas adults typically have 32 teeth.
3. Types of Teeth: Dogs have larger canine teeth for gripping and holding prey, while humans have more molars for grinding food.
4. Growth: Dog teeth grow continuously throughout their lives, whereas human teeth do not.
5. Dental Structure: Dog enamel is thicker than human enamel, helping them withstand the wear from their carnivorous diet.
What Types of Teeth Do Dogs Have?
Dogs have four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
1. Incisors: Small, flat teeth at the front used for grasping and nibbling.
2. Canines: Sharp, pointed teeth next to incisors, used for tearing food.
3. Premolars: Flat-topped teeth behind canines, designed for grinding and shearing.
4. Molars: Larger, flat teeth at the back for crushing and grinding food.
These teeth work together for a dog’s varied diet.
How Sharp Are a Dog's Teeth Compared to Other Animals?
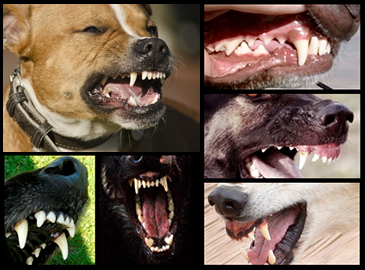
A dog’s teeth are sharp and designed for tearing and grinding, similar to those of other carnivorous animals. Their canine teeth can be particularly sharp, measuring around 1-2 inches in length. Compared to cats, dogs have slightly less sharp teeth but more molars for grinding food. When compared to animals like sharks or crocodiles, dogs' teeth are less sharp but more versatile for their omnivorous diet. Overall, while sharp, a dog’s teeth are optimized for their specific dietary needs rather than sheer sharpness.
What Are the Risks of Dog Bite Injuries?

The risks of dog bite injuries include:
1. Physical Injury: Dog bites can cause severe wounds, infections, and in some cases, amputations or permanent damage.
2. Emotional Trauma: Victims may experience anxiety, fear of dogs, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
3. Legal Consequences: Dog owners may face lawsuits or liability claims if their dog injures someone.
4. Medical Costs: Treatment for dog bites can be expensive, including emergency care, surgeries, and rehabilitation.
5. Risk of Disease: Dog bites can transmit infections such as rabies or tetanus if not properly treated.
How to Care for Your Dog's Teeth and Gums?
To care for your dog's teeth and gums:
1. Brush Regularly: Use a dog-specific toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush. Aim for brushing at least 2-3 times a week.
2. Dental Chews: Provide dental chews that help reduce plaque and tartar buildup.
3. Routine Vet Checkups: Schedule regular veterinary dental cleanings and checkups to catch any issues early.
4. Monitor Diet: Choose high-quality dog food that promotes dental health. Avoid sugary treats.
5. Use Water Additives: Consider dental water additives that help reduce bacteria and plaque.
6. Check for Signs of Trouble: Look for bad breath, swollen gums, or difficulty eating, and consult a vet if any are present.
When Do Puppies Get Their Sharp Teeth?

Puppies typically get their sharp teeth between 2 to 4 weeks of age. By 6 months, they have usually lost their baby teeth and the adult teeth have fully emerged.
Can Sharp Dog Teeth Indicate Aggression?
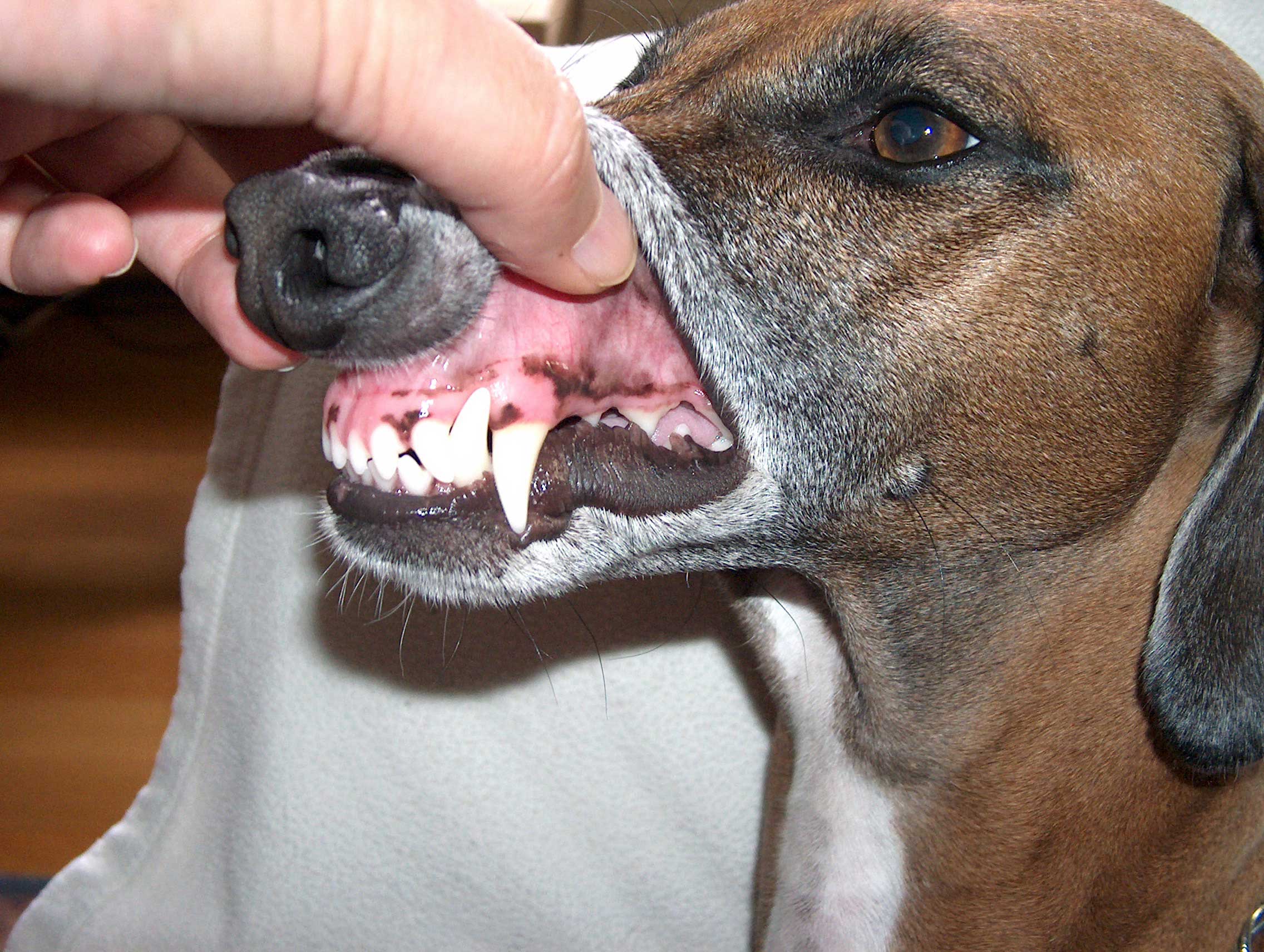
Yes, sharp dog teeth can indicate aggression, but they are not solely a sign of it. Dogs naturally have sharp teeth for biting and tearing, essential for their survival and feeding. Aggression may be expressed through behaviors like growling or baring teeth, but sharp teeth alone do not determine a dog's temperament. Context, body language, and the dog's overall behavior are crucial in assessing aggression.
How Can You Train a Dog to Avoid Biting?
To train a dog to avoid biting, follow these steps:
1. Socialization: Expose your dog to various people and environments from a young age to reduce fear-based biting.
2. Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog with treats and praise for calm behavior and when they refrain from biting.
3. Teach “Leave It” and “No” Commands: Use these commands consistently to discourage unwanted biting behavior.
4. Redirect Behavior: If your dog bites, redirect their attention to a toy or chew item.
5. Time-Outs: If biting occurs, calmly remove your dog from the situation for a brief time-out to signal that biting leads to loss of playtime.
6. Avoid Rough Play: Discourage games that encourage biting, like tug-of-war, to prevent reinforcing aggressive behavior.
7. Consult a Professional: If biting persists, seek help from a certified dog trainer or behaviorist for tailored strategies.
What Are the Common Dental Problems in Dogs?
Common dental problems in dogs include:
1. Periodontal Disease: Inflammation and infection of the gums, often caused by plaque buildup.
2. Tooth Decay: Cavities can develop from bacteria and poor oral hygiene.
3. Broken Teeth: Can occur from chewing hard objects or trauma.
4. Gingivitis: Early stage of gum disease, characterized by redness and swelling.
5. Tartar Buildup: Hard plaque that leads to further dental issues if not removed.
6. Oral Tumors: Abnormal growths in the mouth that can affect overall health.
7. Malocclusion: Misalignment of teeth, which can cause pain and difficulty eating.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can help prevent these issues.
How to Identify a Dog with Dental Issues?
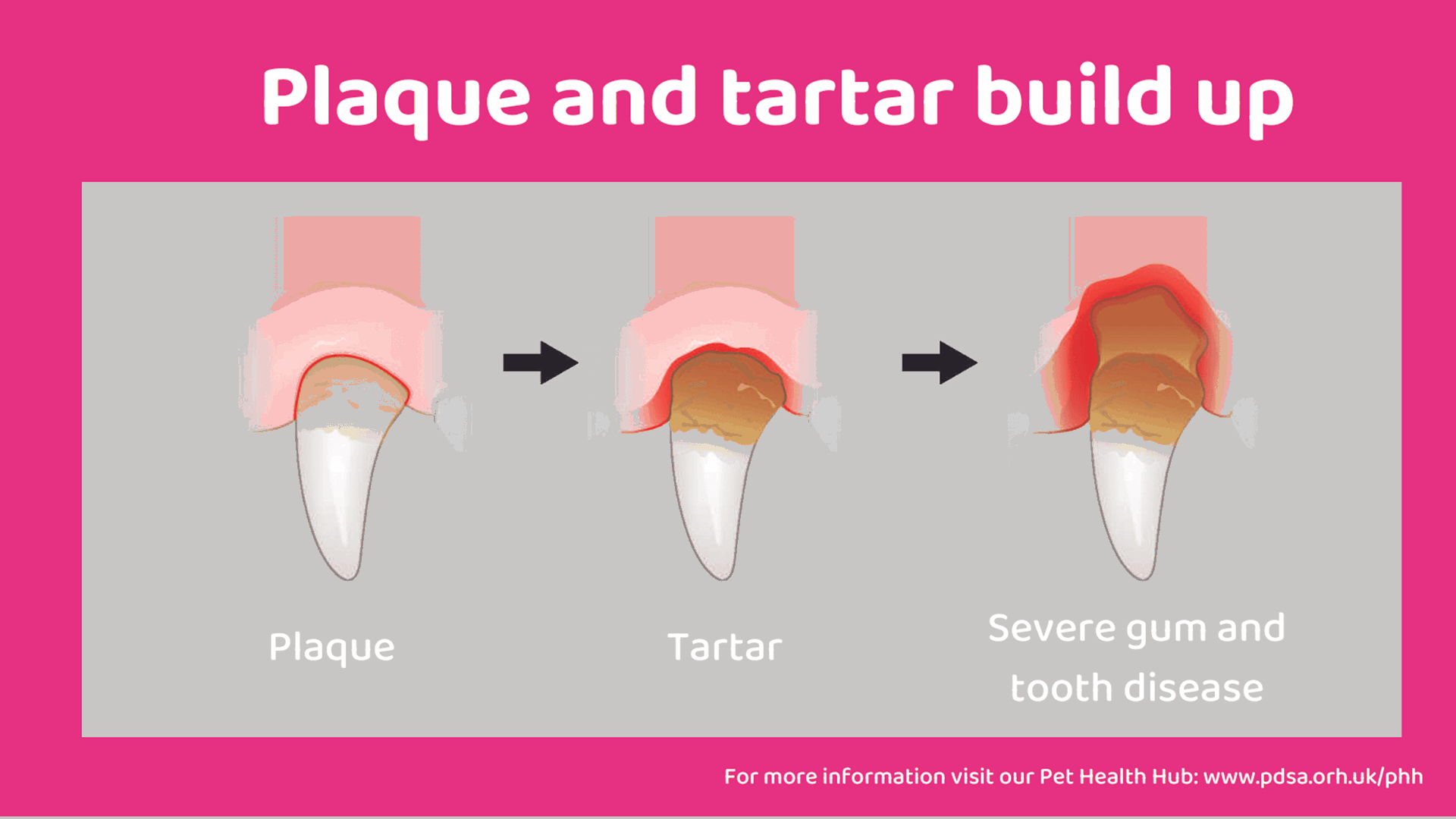
To identify a dog with dental issues, look for the following signs:
1. Bad Breath: Persistent foul odor from the mouth.
2. Gum Inflammation: Red or swollen gums.
3. Excessive Drooling: Increased saliva production.
4. Difficulty Eating: Hesitation or pain while chewing.
5. Loose or Missing Teeth: Noticeable tooth loss or mobility.
6. Pawing at Mouth: Dogs may rub their face or paw at their mouth.
7. Change in Behavior: Increased irritability or reluctance to play.
Regular dental check-ups can help prevent these issues.
What Foods Help Keep a Dog's Teeth Healthy?

Foods that help keep a dog's teeth healthy include:
1. Raw Vegetables: Carrots and celery can help clean teeth and freshen breath.
2. Apples: Crunchy apples can reduce plaque buildup.
3. Sweet Potatoes: These are healthy and can help scrub teeth.
4. Dental Chews: Specially designed chews can promote oral health.
5. Raw Bones: Raw meat bones provide natural abrasion for cleaning teeth.
6. Fish: Omega-3 fatty acids in fish support gum health.
Incorporating these foods can contribute to better dental hygiene for dogs.
How Often Should You Brush Your Dog's Teeth?
You should brush your dog's teeth at least two to three times a week. Daily brushing is ideal for optimal dental health.
What Are the Signs of Tooth Pain in Dogs?

Signs of tooth pain in dogs include:
1. Difficulty eating or chewing.
2. Drooling or excessive saliva.
3. Bad breath.
4. Swollen or bleeding gums.
5. Pawing at the mouth or face.
6. Whining or whimpering when eating.
7. Behavioral changes, such as aggression or withdrawal.
8. Reluctance to play or chew toys.
If you notice these signs, consult a veterinarian for an evaluation.
How Do Dogs Use Their Teeth in Play and Hunting?
Dogs use their teeth in play and hunting primarily for grabbing, tugging, and biting. In play, they often engage in mock battles, using their teeth to gently nip and wrestle with other dogs or toys. During hunting, dogs use their sharp teeth to catch, hold, and tear prey, demonstrating their natural instincts and hunting skills. Their teeth are essential for both enjoyment and survival, allowing for effective communication and interaction with their environment.
Conclusion about # Canines: The Sharp Teeth Explained
In summary, understanding the anatomy and function of canine teeth is essential for responsible pet ownership. Sharp teeth serve vital roles in a dog's diet and behavior, while proper dental care can prevent common health issues. Regular brushing, a balanced diet, and awareness of dental problems can significantly enhance your dog's overall wellbeing. For more detailed insights on canine dental health, explore resources from Tooth1.

