Did you know that humans share about 60% of their DNA with bananas? Just like our fruity friends, our teeth also have unique structures that play a critical role in our dental health. This article delves into the fascinating world of tooth anatomy, covering the essential structures and their functions, how teeth develop over time, and the impact of enamel and dentin on our overall dental well-being. We explore cavity formation, the importance of the pulp chamber, and how different tooth types contribute to our oral health. Additionally, we discuss the relationship between gum tissue and tooth anatomy, the effects of alignment, and common dental issues that can arise. Understanding these aspects not only highlights the significance of proper oral hygiene but also aids in enhancing dental treatments. Join Tooth1 as we unravel how tooth anatomy influences your dental health and the importance of maintaining those pearly whites!
What are the basic structures of tooth anatomy?
The basic structures of tooth anatomy include:
1. Enamel: The hard, outer layer that protects the tooth.
2. Dentin: The layer beneath enamel, softer than enamel, and contains nerve endings.
3. Pulp: The innermost part containing nerves and blood vessels.
4. Cementum: A bone-like tissue that covers the tooth root, helping anchor it in the jawbone.
5. Periodontal Ligament: Connective tissue that surrounds the root and attaches the tooth to the jawbone.
How do teeth develop and change over time?
Teeth develop from the embryonic stage, starting as dental lamina, which forms tooth buds. These buds grow into primary teeth, typically emerging between 6 months to 3 years. As children grow, their jaws expand, allowing for the development of permanent teeth, which begin forming under the gums around age 6.
Over time, teeth undergo changes due to wear, decay, and environmental factors. They can shift position as bone structure changes, often influenced by habits like thumb-sucking or teeth grinding. Aging also leads to enamel wear and potential gum recession, affecting dental health. Proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are crucial for maintaining tooth health throughout these changes.
What role do enamel and dentin play in dental health?
Enamel protects teeth from decay and damage, providing a hard outer layer that resists wear. Dentin, located beneath the enamel, supports the tooth structure and contains nerve endings. Together, they contribute to overall dental health by safeguarding against cavities and sensitivity.
How does tooth anatomy influence cavity formation?
Tooth anatomy influences cavity formation primarily through the structure and composition of enamel, dentin, and the tooth's overall morphology.
1. Enamel Thickness: Thinner enamel is less protective against acid attacks, making teeth more susceptible to cavities.
2. Dentin Structure: Dentin is softer than enamel. If enamel is compromised, cavities can progress quickly into dentin, which is more porous and allows bacteria to proliferate.
3. Pit and Fissure Depth: Deep pits and fissures in molars can trap food and bacteria, increasing the risk of cavity formation.
4. Tooth Alignment: Misaligned teeth can create areas that are difficult to clean, promoting plaque accumulation and cavity development.
5. Root Anatomy: Exposed roots due to gum recession are more vulnerable to decay as they lack the protective enamel covering.
Overall, the specific anatomical features of teeth directly impact their vulnerability to cavities and the effectiveness of oral hygiene practices.
What is the significance of the pulp chamber in tooth health?
The pulp chamber is significant for tooth health because it houses the dental pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels vital for tooth vitality and sensation. It helps maintain the tooth's structure and provides nutrients. Damage or infection in the pulp chamber can lead to pain, abscesses, and tooth loss, emphasizing its critical role in overall dental health.
How do different tooth types affect overall dental function?
Different tooth types affect overall dental function as follows:
1. Incisors: Sharp edges for cutting food. They facilitate the initial bite.
2. Canines: Pointed for tearing food. They play a crucial role in the bite force and alignment.
3. Premolars: Flat surfaces for grinding food. They assist in crushing and breaking down food before swallowing.
4. Molars: Broad and strong for grinding. They are essential for thorough mastication, impacting digestion and nutrient absorption.
The combination of these tooth types ensures efficient chewing, aids in proper digestion, and influences overall oral health.
How does gum tissue relate to tooth anatomy?
Gum tissue, or gingiva, supports tooth anatomy by anchoring teeth in the jawbone and protecting the roots. Healthy gum tissue forms a seal around teeth, preventing bacteria from entering the periodontal pockets. This relationship is crucial for overall dental health; compromised gum tissue can lead to periodontal disease, which affects tooth stability and health. Proper gum health supports tooth structure and function, influencing overall dental well-being.
What impact does tooth alignment have on dental health?

Tooth alignment significantly impacts dental health by affecting bite function, leading to issues like tooth wear, jaw pain, and gum disease. Misaligned teeth can create areas that are difficult to clean, increasing the risk of cavities and periodontal disease. Proper alignment promotes efficient chewing and reduces strain on jaw muscles, contributing to overall oral health.
How do root structures contribute to tooth stability?
Root structures contribute to tooth stability by anchoring the tooth within the jawbone. The roots, which are embedded in the alveolar bone, provide support and distribute forces during chewing. The periodontal ligament surrounding the roots helps absorb shocks and allows slight movement, enhancing stability. Additionally, the shape and depth of the roots influence how well a tooth can withstand stresses, making them crucial for overall dental health.
What are common dental issues related to tooth anatomy?
Common dental issues related to tooth anatomy include:
1. Cavities: Decay can occur in pits and fissures on the tooth surface.
2. Gum Disease: Poor tooth alignment can lead to plaque buildup and inflammation.
3. Tooth Sensitivity: Exposed dentin, often due to enamel wear, causes discomfort.
4. Malocclusion: Misalignment affects bite and can lead to jaw pain.
5. Cracked Teeth: Structural weaknesses in enamel increase the risk of fractures.
6. Periodontal Problems: Tooth roots' exposure can result in gum recession.
Understanding these issues highlights the importance of tooth anatomy in maintaining dental health.
How does tooth anatomy vary among different individuals?
Tooth anatomy varies among individuals in several ways:
1. Size: Tooth dimensions can differ significantly, affecting bite and alignment.
2. Shape: Variations in the shape of crowns and roots influence occlusion and aesthetics.
3. Number: Some people have extra teeth (hyperdontia) or missing teeth (hypodontia).
4. Eruption Patterns: Timing and sequence of tooth eruption can vary, impacting dental health.
5. Enamel Thickness: Variations in enamel thickness affect susceptibility to decay and sensitivity.
These differences can influence overall dental health, including issues with alignment, decay risk, and the need for orthodontic treatment.
## How Do Donkey Teeth Structure and Anatomy Impact Their Dental Health?
Tooth anatomy affects dental health by influencing how teeth align, how well they can be cleaned, and their susceptibility to decay and gum disease. For example, irregularities in tooth shape or size, such as those seen with donkey teeth, can create pockets for plaque buildup, leading to increased dental issues. Proper tooth structure ensures effective chewing and maintains overall oral health.
Learn more about donkey teeth
What is the relationship between tooth anatomy and oral hygiene?
Tooth anatomy directly influences oral hygiene practices. The shape and structure of teeth, including grooves, pits, and interproximal spaces, determine how easily plaque can accumulate. Molars, with their cusps and fissures, are more prone to cavities, requiring thorough brushing and flossing. Additionally, the alignment of teeth affects how well they can be cleaned; crowded or misaligned teeth create hidden areas where food and bacteria can thrive, increasing the risk of gum disease. Proper understanding of tooth anatomy can help in choosing effective oral hygiene techniques to maintain dental health.
How can understanding tooth anatomy improve dental treatments?
Understanding tooth anatomy improves dental treatments by enabling precise diagnosis and targeted interventions. Knowledge of enamel, dentin, pulp, and root structures helps dentists tailor procedures like fillings, crowns, and root canals. It enhances the ability to identify issues such as cavities or infections early, leading to more effective treatments. Additionally, understanding anatomical variations allows for personalized care, improving patient outcomes and satisfaction.
What are the effects of tooth decay on dental structure?
Tooth decay leads to the demineralization of enamel, causing cavities that can weaken the tooth structure. As decay progresses, it can penetrate the dentin, increasing sensitivity and pain. If untreated, decay can reach the pulp, leading to infection and potential tooth loss. Overall, tooth decay compromises the integrity, function, and health of the dental structure.
How does tooth wear and tear affect dental health?
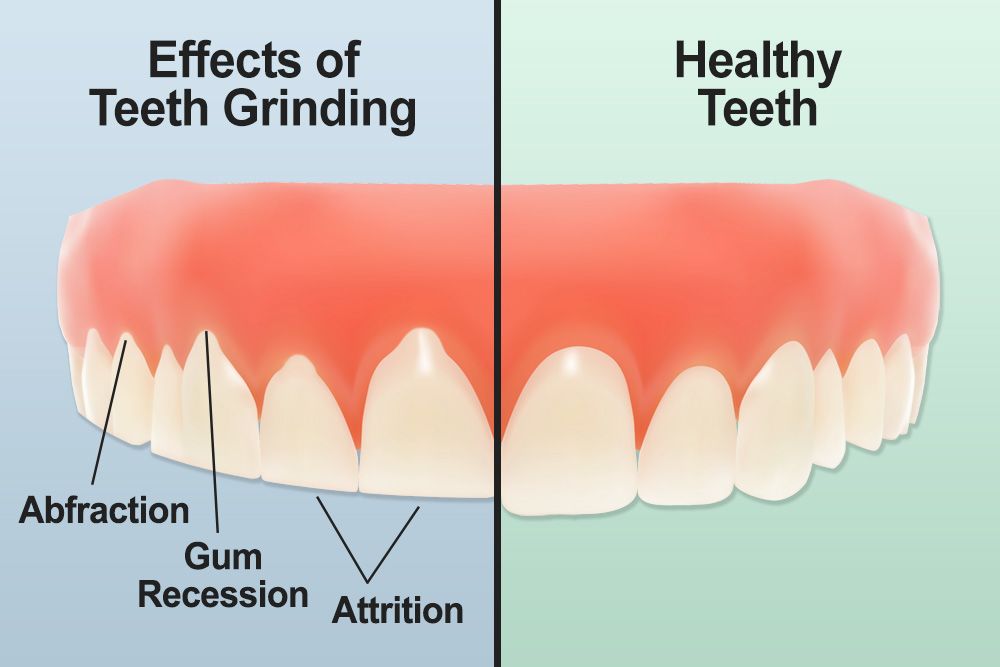
Tooth wear and tear can lead to various dental health issues, including sensitivity, cavities, and increased risk of fractures. As enamel erodes, teeth become more vulnerable to decay and damage. This can also affect bite alignment and lead to jaw pain or headaches. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene can help mitigate these effects.
How can dental professionals assess tooth anatomy for better care?
Dental professionals can assess tooth anatomy for better care by:
1. Utilizing Radiographs: X-rays reveal internal structures, aiding in the diagnosis of decay, fractures, and anomalies.
2. Conducting Clinical Exams: Visual and tactile examinations help identify surface irregularities and wear patterns.
3. Studying Tooth Morphology: Understanding variations in size and shape assists in treatment planning and restoration.
4. Using Dental Models: Physical or digital models provide insights into occlusion and alignment.
5. Incorporating Technology: CAD/CAM systems enable precise assessment and customization of dental restorations based on tooth anatomy.
These methods enhance understanding of tooth anatomy, leading to improved dental health outcomes.
Conclusion about # How Does Tooth Anatomy Affect Dental Health?
Understanding tooth anatomy is crucial for maintaining optimal dental health. Key structures like enamel and dentin play vital roles in protecting against cavities, while the pulp chamber is essential for overall tooth vitality. Different tooth types and their alignment significantly influence functionality and stability, impacting oral hygiene practices. Awareness of common dental issues related to tooth anatomy allows for proactive care. By leveraging this knowledge, both patients and dental professionals can enhance treatment outcomes. For more in-depth information and guidance, reach out to Tooth1.