Did you know that the average person spends 38.5 days brushing their teeth over a lifetime? While that might seem like a lot of time, understanding the connection between teeth types and nutrition is crucial for a healthy lifestyle. This article dives into how different teeth types—incisors, canines, and molars—impact our eating habits and nutritional health. We'll explore the roles each tooth plays in digestion, the nutrients essential for maintaining strong teeth, and how misalignment can affect your diet. Additionally, discover how age influences our dental structure and nutritional needs, as well as the best practices for oral care that can enhance your overall health. Join us at Tooth1 as we uncover these vital connections!
How Do Different Teeth Types Affect Nutrition?
Different teeth types—incisors, canines, premolars, and molars—play specific roles in nutrition.
1. Incisors: Sharp and flat, they cut food, making it easier to chew and digest.
2. Canines: Pointed and strong, they tear food, especially meat, aiding in protein intake.
3. Premolars: Flat surfaces help grind and crush food, enhancing nutrient absorption.
4. Molars: These large teeth thoroughly grind food, facilitating digestion and nutrient extraction.
Overall, the structure and function of each tooth type directly influence how effectively food is processed and nutrients are absorbed.
What Role Do Incisors Play in Eating?
Incisors are the front teeth used primarily for cutting and slicing food. They play a crucial role in the initial stages of eating by breaking down food into smaller, manageable pieces, making it easier to chew and digest. Their sharp edges facilitate this cutting action, essential for consuming various foods, particularly fruits and vegetables.
Why Are Canines Important for Chewing?
Canines are important for chewing because they are designed for tearing food, particularly meat. Their pointed shape helps grip and shred tough textures, facilitating the breakdown of food into smaller, digestible pieces. This action is crucial for proper nutrition, as it aids in the digestion and absorption of nutrients. Additionally, canines play a role in maintaining oral health by promoting balanced wear of teeth and preventing plaque buildup.
How Do Molars Contribute to Digestive Health?
Molars contribute to digestive health by efficiently grinding and crushing food, which aids in mechanical digestion. This process increases the surface area of food, making it easier for enzymes to break down nutrients during chemical digestion in the stomach and intestines. Healthy molars help prevent issues like food particles remaining undigested, leading to better nutrient absorption and overall digestive health.
What Nutrients Are Best for Healthy Teeth?
Calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D are essential nutrients for healthy teeth. Calcium strengthens tooth enamel, phosphorus aids in the remineralization process, and vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium effectively. Additionally, vitamin C supports gum health, while fluoride promotes enamel strength. A balanced diet including dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, fish, and fruits can provide these vital nutrients.
How Can Tooth Misalignment Impact Nutrition?
Tooth misalignment can restrict proper chewing, making it difficult to break down food, which may lead to poor digestion and nutrient absorption. It can also cause discomfort or pain while eating, leading to a preference for softer, less nutritious foods. Additionally, misaligned teeth can contribute to uneven wear and increased risk of cavities, further compromising nutritional intake.
What Foods Promote Strong Teeth and Gums?

Foods that promote strong teeth and gums include:
1. Dairy Products: Cheese, yogurt, and milk provide calcium and phosphate, essential for tooth enamel strength.
2. Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale are rich in vitamins and minerals that support gum health.
3. Crunchy Fruits and Vegetables: Apples, carrots, and celery stimulate saliva production, helping to wash away food particles and bacteria.
4. Nuts and Seeds: Almonds and sunflower seeds are high in calcium and healthy fats, promoting overall oral health.
5. Fatty Fish: Salmon and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation in the gums.
6. Green Tea: Contains compounds that can inhibit bacteria and reduce the risk of gum disease.
7. Whole Grains: Brown rice and whole wheat bread provide nutrients that support gum health.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help maintain strong teeth and gums.
How Does Teeth Type Influence Food Choices?
Teeth type influences food choices by determining what foods can be easily processed. For instance, carnivores have sharp, pointed teeth for tearing meat, leading them to prefer high-protein diets. Herbivores possess flat molars for grinding plant materials, guiding them toward fibrous foods. Humans, with a mixed dentition of incisors, canines, and molars, can consume a diverse diet, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and proteins. Overall, teeth type shapes dietary habits based on the ability to chew and digest different food types effectively.
What Are the Effects of Missing Teeth on Diet?
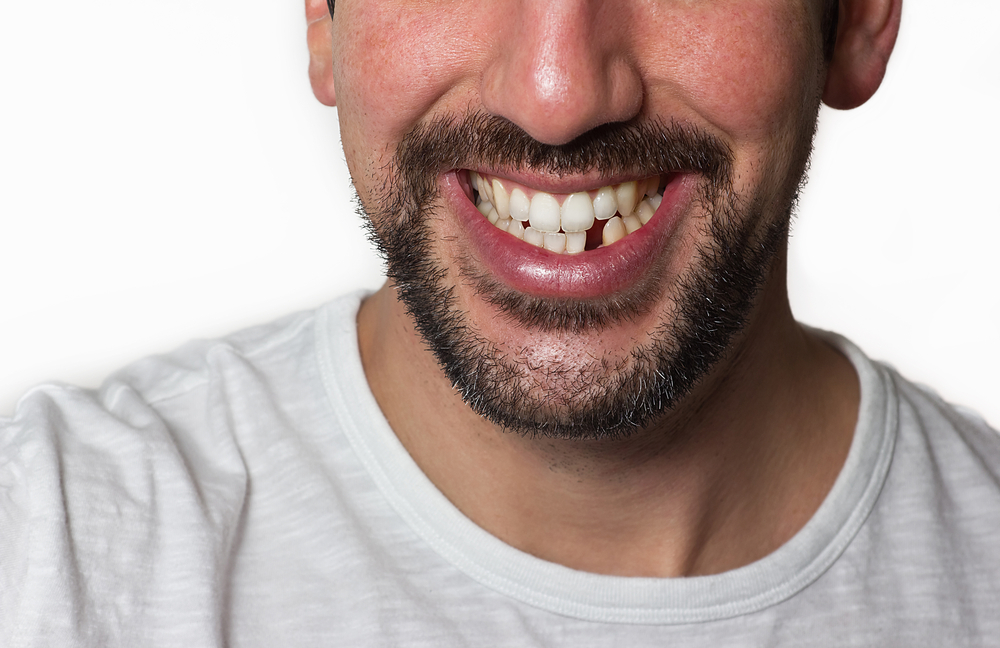

Missing teeth can significantly impact diet by making it difficult to chew certain foods, leading to a preference for softer, less nutritious options. This can result in imbalanced nutrition, as individuals may avoid fruits, vegetables, and proteins that require more chewing. Additionally, missing teeth can affect bite alignment and jaw function, causing discomfort while eating and potentially leading to digestive issues from inadequate mastication. Overall, the absence of teeth can restrict dietary variety and quality, negatively influencing overall health.
How Can Dental Health Affect Nutritional Intake?
Dental health directly impacts nutritional intake by influencing the ability to chew and digest food. Poor dental health, such as cavities or gum disease, can cause pain and discomfort, leading to avoidance of certain foods, particularly hard or crunchy items. This may result in a limited diet, lacking essential nutrients. Additionally, missing teeth or dentures can alter eating habits, affecting overall nutrition and health. Maintaining good dental hygiene is crucial for preserving teeth and ensuring a varied, balanced diet.
What Teeth Types Are Associated with Specific Diets?
Carnivores typically have sharp, pointed teeth (canines) for tearing flesh and flat molars for grinding. Herbivores possess flat, broad molars for grinding plant material and less pronounced canines. Omnivores have a mix of sharp and flat teeth, allowing them to consume both plants and animals effectively.
## How Do Donkey Teeth Types Affect Their Nutrition?
Donkey teeth are adapted for a herbivorous diet, allowing them to efficiently grind fibrous plant material. The type of teeth in donkeys, including incisors and molars, play a crucial role in their ability to break down tough forage, which is essential for their nutrition. Proper dental health is vital for donkeys to effectively chew and digest their food.
Learn more about donkey teeth
How Do Teeth Types Affect Food Texture and Chewing?
Teeth types affect food texture and chewing by influencing how food is broken down.
1. Incisors: Sharp and flat, incisors slice through food, making them essential for cutting fruits and vegetables.
2. Canines: Pointed and strong, canines tear food, particularly meat, allowing for a more effective grip.
3. Premolars: Broad and flat, premolars crush and grind food, aiding in the reduction of larger pieces into smaller, manageable bits.
4. Molars: Larger and more robust, molars provide powerful grinding capabilities, essential for breaking down tough foods like grains and fibrous vegetables.
Different tooth types work together to optimize the chewing process, ensuring efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
What Nutritional Deficiencies Are Linked to Poor Dental Health?
Nutritional deficiencies linked to poor dental health include:
1. Calcium Deficiency: Weakens tooth structure and bones.
2. Vitamin D Deficiency: Impairs calcium absorption, leading to weaker teeth.
3. Vitamin C Deficiency: Increases risk of gum disease and affects healing.
4. Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Linked to gum disease and oral inflammation.
5. Iron Deficiency: May cause glossitis and oral lesions.
6. Phosphorus Deficiency: Affects tooth mineralization.
These deficiencies can lead to various dental issues, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet for oral health.
How Can Proper Oral Care Enhance Nutritional Health?
Proper oral care enhances nutritional health by ensuring efficient chewing and digestion, which aids nutrient absorption. Healthy teeth allow for a varied diet, including fruits, vegetables, and proteins that are essential for overall health. Maintaining oral hygiene prevents dental issues like cavities and gum disease, which can lead to pain and difficulty eating. This facilitation of a balanced diet supports better nutrition and contributes to overall wellness.
What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Healthy Teeth?
1. Choose a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly calcium and vitamin D, to support strong teeth.
2. Limit sugary and acidic foods that can lead to tooth decay and erosion.
3. Drink plenty of water to help wash away food particles and bacteria.
4. Incorporate crunchy fruits and vegetables like apples and carrots, which can help clean teeth naturally.
5. Avoid snacking frequently to reduce the risk of plaque buildup.
6. Maintain regular dental check-ups for professional cleaning and monitoring of oral health.
7. Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent cavities.
How Does Age Affect Teeth Types and Nutritional Needs?
Age affects teeth types and nutritional needs in several ways.
1. Teeth Types: Children have primary teeth that are smaller and shaped differently than adult teeth. As people age, they transition to permanent teeth, which are larger and designed for more complex chewing. Older adults may experience tooth wear, loss, or changes in tooth structure, affecting their ability to chew.
2. Nutritional Needs: Younger individuals typically require nutrients for growth and development, emphasizing calcium and vitamin D for strong teeth. As people age, their nutritional needs shift; older adults may need softer foods that are easier to chew and digest, which can require adjustments in nutrient intake, focusing on fiber, protein, and vitamins to maintain overall health and oral hygiene.
Overall, age influences both the physical structure of teeth and the dietary adjustments necessary for maintaining oral health.
Conclusion about # The Connection Between Teeth Types and Nutrition
In summary, understanding the connection between teeth types and nutrition is crucial for maintaining overall health. Each type of tooth—incisors, canines, and molars—plays a significant role in the eating process, influencing the types of foods we consume and how well we digest them. Proper oral care not only enhances dental health but also supports nutritional intake. To promote strong teeth and gums, it is essential to focus on a balanced diet rich in nutrients. By prioritizing dental health through effective practices and awareness, individuals can optimize their nutritional well-being. For more detailed guidance on maintaining healthy teeth, visit Tooth1.
Sources:
- Nutrition and Oral Health | American Dental Association
- Diet and Nutrition to Prevent Dental Problems - StatPearls - NCBI ...
- Get the Facts: Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and Consumption ...
- Oral health: A window to your overall health - Mayo Clinic
- Relationship between Food Habits and Tooth Erosion Occurrence in ...
- Periodontal Disease and Incident Type 2 Diabetes: Results from the ...

