Did you know that your teeth might have a secret life influenced by hormones? In this article, we dive into the fascinating connection between hormones and teeth growth, exploring how various hormonal changes can affect dental development at different life stages. We'll uncover the impact of sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone on tooth eruption and growth, discuss the influences of thyroid hormones, and examine how changes during puberty and pregnancy can affect dental health. Additionally, we'll address the implications of hormonal imbalances, menopause, and even diet on oral health. With insights from Tooth1, you'll learn preventive measures to maintain your dental health amid these hormonal shifts.
How do hormones influence tooth development?
Hormones influence tooth development by regulating the growth and differentiation of dental tissues. Key hormones include:
1. Growth Hormone (GH): Stimulates overall growth and affects the development of dental tissues.
2. Thyroid Hormones (T3 and T4): Essential for the formation of enamel and dentin, influencing the timing of tooth eruption.
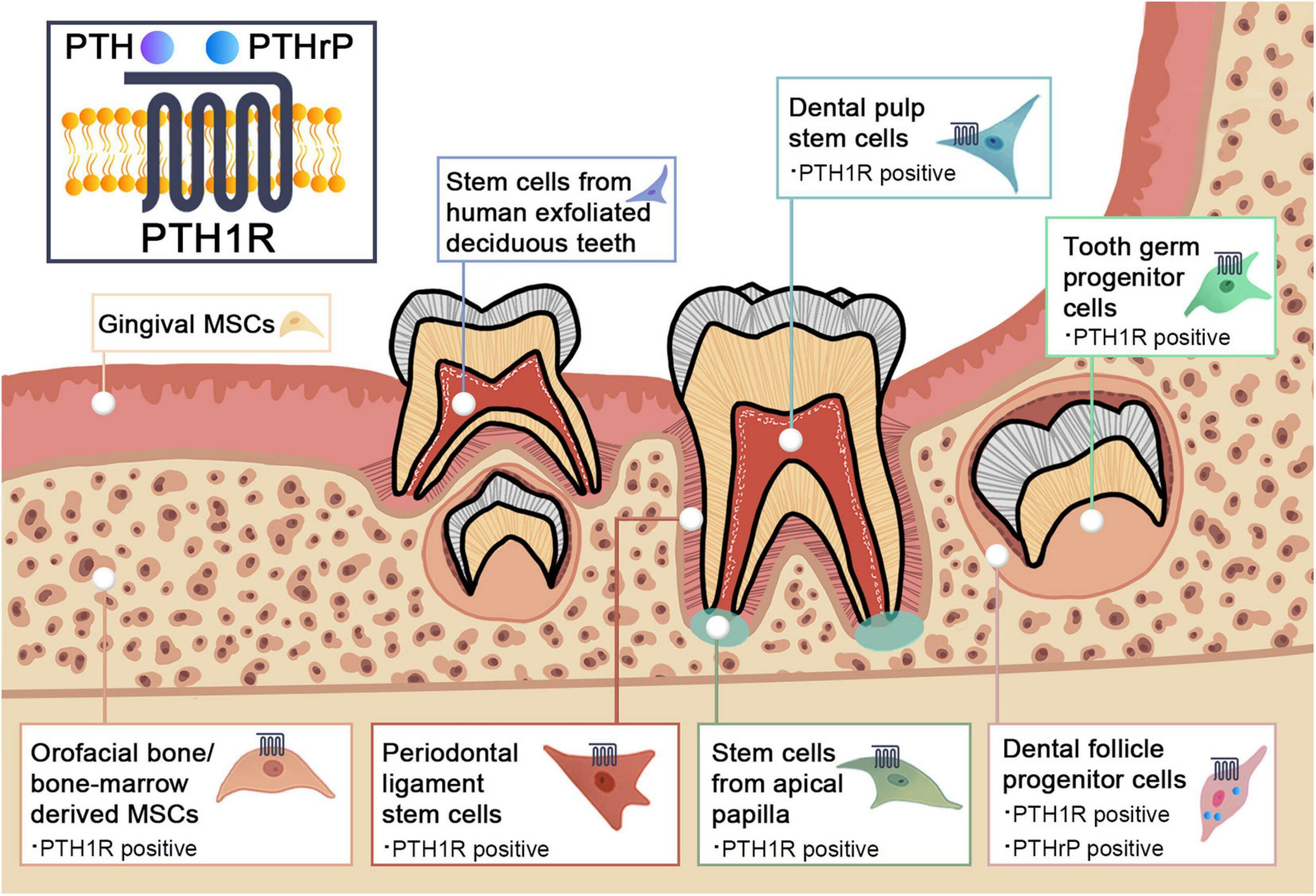
3. Sex Hormones (Estrogen and Testosterone): Affect the development of dental structures and can influence the timing of dental maturation, particularly during puberty.
4. Insulin: Plays a role in nutrient metabolism, impacting the health of dental tissues.
These hormones work together to ensure proper tooth formation, eruption, and overall oral health.
What role do sex hormones play in dental growth?
Sex hormones, particularly estrogen and testosterone, influence dental growth by regulating the development and maturation of dental tissues. Estrogen promotes the proliferation of dental pulp cells and affects the formation of enamel and dentin, while testosterone influences the timing of tooth eruption. These hormones also impact jawbone growth and density, which are crucial for proper alignment and spacing of teeth. Overall, sex hormones play a vital role in the timing and quality of dental development.
Can hormonal changes affect dental health in children?
Yes, hormonal changes can affect dental health in children. During puberty, increased hormone levels can lead to changes in saliva production, gum tissue, and the risk of periodontal disease. These hormonal fluctuations may also influence the timing of tooth eruption and overall oral hygiene practices.
How does estrogen impact tooth eruption in females?
Estrogen influences tooth eruption in females by promoting the development and maturation of dental tissues. It enhances blood flow to the gums and stimulates the production of growth factors, which can accelerate the timing of tooth eruption. Additionally, estrogen helps regulate the activity of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, impacting bone remodeling around the teeth. This hormonal effect is particularly notable during puberty and menstrual cycles, where fluctuations in estrogen levels can lead to variations in dental growth and eruption patterns.
What is the relationship between testosterone and dental growth?
Testosterone influences dental growth by promoting the development of the jaw and teeth. It enhances bone density, which supports tooth eruption and alignment. Additionally, testosterone may affect the timing of dental maturation, with higher levels potentially leading to earlier tooth development. Overall, testosterone plays a significant role in the growth and health of dental structures.
Are there hormonal factors that delay tooth growth?
Yes, hormonal factors can delay tooth growth. Hormones such as growth hormone, thyroid hormones, and sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone) play critical roles in dental development. Imbalances or deficiencies in these hormones can lead to delayed eruption and development of teeth. For instance, hypothyroidism can slow down overall growth, including teeth, while growth hormone deficiencies can impact the timing of tooth eruption.
How do thyroid hormones affect teeth development?
Thyroid hormones, particularly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), play a crucial role in teeth development by regulating the growth and maturation of dental tissues. They influence the formation of enamel and dentin, impact the eruption of teeth, and affect the overall metabolism of bone structures supporting teeth. An imbalance in thyroid hormone levels can lead to dental issues, including delayed eruption, enamel hypoplasia, and altered tooth morphology.
What hormonal changes occur during puberty that influence teeth?
During puberty, hormonal changes significantly affect teeth growth. Increased levels of sex hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, stimulate the development of jawbone and dental tissues, leading to the eruption of permanent teeth. Additionally, growth hormone contributes to the overall growth of the jaw, which can alter tooth alignment. Hormonal fluctuations can also impact saliva production, affecting oral health and the risk of cavities.
Can pregnancy hormones affect dental health?
Yes, pregnancy hormones can affect dental health. Increased levels of hormones like estrogen and progesterone can lead to changes in the gums, causing pregnancy gingivitis, which results in inflammation and bleeding. Hormonal fluctuations may also affect saliva production and increase the risk of cavities. Regular dental check-ups during pregnancy are essential for maintaining oral health.
How do hormonal imbalances impact oral health?
Hormonal imbalances can significantly affect oral health through various mechanisms. Changes in hormone levels, especially estrogen and progesterone, can lead to gum inflammation and increased sensitivity, resulting in conditions like gingivitis. Hormonal fluctuations can also affect saliva production, leading to dry mouth, which increases the risk of cavities and periodontal disease. Additionally, hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can alter the body's response to dental plaque, making oral hygiene more critical during these times.
What are the effects of menopause on dental health?
Menopause can lead to several dental health issues due to hormonal changes. Common effects include:
1. Dry Mouth: Decreased estrogen levels can reduce saliva production, leading to dry mouth, which increases the risk of cavities and gum disease.
2. Gum Disease: Hormonal fluctuations can cause gums to become more sensitive and prone to inflammation, increasing the likelihood of gingivitis and periodontal disease.
3. Bone Density Loss: Reduced estrogen can weaken jawbone density, affecting tooth stability and increasing the risk of tooth loss.
4. Changes in Taste: Hormonal changes may alter taste perception, affecting dietary choices and potentially leading to poor nutrition, which can impact oral health.
5. Oral Candidiasis: Women may be more susceptible to oral thrush due to hormonal changes, which can cause discomfort and affect oral hygiene.
Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene are essential during menopause to mitigate these effects.
How can hormone therapy influence teeth growth?

Hormone therapy can influence teeth growth by altering the balance of hormones like estrogen and testosterone, which play a crucial role in bone and dental health. Increased estrogen can enhance jawbone density and promote proper alignment of teeth. Conversely, hormonal imbalances may lead to conditions like osteoporosis, negatively affecting tooth support structures. Additionally, hormone therapy can impact saliva production, influencing oral health and potentially affecting tooth development.
Do growth hormones affect adult teeth development?
Yes, growth hormones can affect adult teeth development. They influence the growth and maturation of dental structures, impacting the timing and quality of tooth eruption and alignment. Elevated hormone levels may lead to issues such as malocclusion or delayed eruption.
What signs indicate hormonal issues affecting teeth?
Signs indicating hormonal issues affecting teeth include:
1. Delayed Tooth Development: Teeth erupting later than expected.
2. Gum Problems: Swelling, bleeding, or sensitivity in gums.
3. Tooth Decay: Increased cavities or rapid deterioration of tooth enamel.
4. Jaw Issues: Changes in jaw alignment or pain, possibly due to hormonal imbalances.
5. Dental Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli.
6. Changes in Oral Health: Frequent infections, dry mouth, or changes in saliva production.
7. Abnormal Growth: Development of extra teeth or absence of teeth.
Consult a dentist if you notice these signs.
How can diet impact hormone levels and dental health?
Diet impacts hormone levels by influencing the production of hormones like insulin, cortisol, and estrogen. High sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, affecting overall hormonal balance. Nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids support hormone regulation and are essential for dental health.
Inadequate nutrition can weaken teeth and gums, increasing the risk of dental issues. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains promotes hormonal health and strengthens teeth. Conversely, diets high in processed foods and sugars can lead to inflammation, negatively affecting both hormones and dental health.
What preventive measures can maintain dental health during hormonal changes?
To maintain dental health during hormonal changes, consider the following preventive measures:
1. Regular Dental Visits: Schedule check-ups and cleanings to monitor oral health.
2. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily and floss to prevent plaque buildup.
3. Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly calcium and vitamin D.
4. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep gums moist and reduce dry mouth.
5. Use Fluoride Products: Incorporate fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash to strengthen enamel.
6. Avoid Sugary Foods: Limit sugar intake to reduce the risk of cavities.
7. Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques, as stress can impact oral health.
8. Consider Hormonal Changes: Be aware of how hormonal fluctuations (like pregnancy or menopause) can affect gums and teeth, and adjust care accordingly.
Conclusion about # Understanding the Impact of Hormones on Teeth Growth
Hormones play a crucial role in tooth growth and overall dental health throughout various life stages. Their influence is particularly evident during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, as well as in the presence of hormonal imbalances. Understanding these connections can help in identifying potential dental issues early on and seeking appropriate interventions. Maintaining a balanced diet and considering preventive dental measures are vital for supporting dental health in relation to hormonal changes. For more comprehensive insights and support, Tooth1 is here to help you navigate the complexities of dental care.