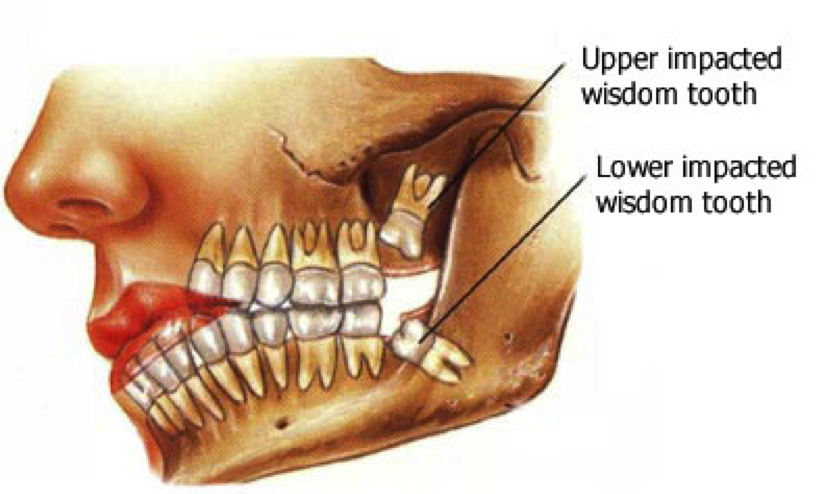
Did you know that your teeth are only as strong as the bond they share with your jaw? In this article, we explore the fascinating connection between teeth and the jawbone, highlighting how they are anchored together and the vital role of the periodontal ligament in maintaining stability. We'll delve into the anatomy of this connection, the impact of jaw alignment on oral health, and what happens when teeth loosen. Additionally, we discuss treatments for loose teeth, the influence of bone density on stability, and how dental implants integrate with the jaw. Finally, discover the relationship between nutrition and jaw health, all brought to you by Tooth1, your go-to source for in-depth dental information.
How are teeth anchored to the jawbone?
Teeth are anchored to the jawbone through structures called periodontal ligaments. These ligaments connect the tooth roots to the alveolar bone, providing support and stability. The roots of the teeth are embedded in sockets within the jawbone, and the periodontal ligaments allow for slight movement while absorbing shock during chewing. Additionally, the connection is reinforced by cementum, a calcified tissue covering the tooth roots.
What role does the periodontal ligament play in tooth stability?
The periodontal ligament (PDL) secures teeth to the jawbone, providing stability and support. It acts as a cushion, absorbing forces from chewing and preventing excessive movement. The PDL also facilitates the transmission of sensory signals and aids in the regeneration of tissue, contributing to overall dental health.
## How Are Donkey Teeth Connected to Their Jaw?
Teeth are connected to the jaw by the periodontal ligament, which anchors them in their sockets. This ligament attaches the tooth root to the jawbone, providing stability and support. The jawbone itself, particularly the alveolar bone, holds the teeth in place.
Learn more about donkey teeth
How does the jawbone support teeth?
The jawbone supports teeth by providing a stable foundation through the alveolar bone, which contains sockets for each tooth root. The periodontal ligament connects the tooth roots to the jawbone, allowing for stability while absorbing shock during biting and chewing. This structure ensures that teeth remain securely anchored and aligned within the mouth.
What is the anatomy of teeth and jaw connection?
Teeth are connected to the jaw through the periodontal ligament, which anchors them to the alveolar bone of the jaw. The roots of the teeth fit into sockets in the jawbone, providing stability. The jaw consists of two main parts: the maxilla (upper jaw) and the mandible (lower jaw). The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) connects the mandible to the skull, allowing for movement during chewing and speaking.
How do teeth and jaw alignment affect oral health?
Teeth and jaw alignment directly impact oral health by influencing bite efficiency, wear patterns, and overall dental function. Misaligned teeth can lead to uneven pressure, causing tooth wear, fractures, and jaw pain. Poor jaw alignment may also contribute to issues like temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, headaches, and difficulty chewing. Proper alignment facilitates effective cleaning, reducing the risk of cavities and gum disease. Regular dental check-ups can help address alignment issues and promote better oral health.
What happens when teeth loosen from the jaw?
When teeth loosen from the jaw, it typically indicates underlying issues such as gum disease, bone loss, or trauma. The supportive structures like gums and bone deteriorate, leading to instability. This can cause pain and increase the risk of tooth loss if not addressed promptly.
How do braces affect the connection between teeth and jaw?
Braces apply pressure to teeth, gradually shifting them into proper alignment. This movement affects the connection between teeth and jaw by altering the position of the teeth within the dental arch, which can influence how the teeth fit together and interact with the jawbone. Over time, the jaw may adapt to these changes, improving bite function and overall dental alignment.
What types of dental issues arise from jaw problems?
Jaw problems can lead to several dental issues, including:
1. Misalignment: Malocclusion can cause uneven wear on teeth and lead to tooth decay.
2. TMJ Disorders: Jaw pain can affect biting and chewing, increasing stress on teeth.
3. Tooth Sensitivity: Misaligned jaws can lead to gum recession, exposing tooth roots and causing sensitivity.
4. Cracked or Chipped Teeth: Excessive force from jaw misalignment can result in structural damage to teeth.
5. Gum Disease: Jaw issues can impact oral hygiene, leading to inflammation and infection in the gums.
Addressing jaw problems is crucial for maintaining overall dental health.
How does bone density influence teeth stability?
Bone density significantly influences teeth stability by providing the necessary support for the roots of the teeth within the jawbone. Higher bone density means stronger, healthier bone structure, which better anchors teeth and reduces the risk of tooth mobility or loss. Conversely, low bone density can lead to weakened support, increasing the likelihood of tooth instability and periodontal issues.
What are the signs of unhealthy teeth-jaw connections?
Signs of unhealthy teeth-jaw connections include:
1. Jaw Pain or Discomfort: Pain in the jaw muscles or joints.
2. Difficulty Chewing: Trouble biting or chewing food.
3. Teeth Grinding: Clenching or grinding teeth, especially during sleep.
4. Misaligned Teeth: Teeth that are crooked or do not fit together properly.
5. Frequent Headaches: Recurrent headaches, particularly around the temples.
6. Clicking or Popping Sounds: Noises from the jaw when opening or closing the mouth.
7. Sensitive Teeth: Increased sensitivity in teeth when biting or consuming hot/cold food.
8. Gum Issues: Swelling or bleeding gums, indicating potential underlying problems.
Consult a dental professional if experiencing these symptoms.
How can I strengthen the connection between my teeth and jaw?
To strengthen the connection between your teeth and jaw, focus on these key practices:
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing prevent gum disease, which can weaken the attachment of teeth to the jawbone.
2. Nutrition: Consume a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone health.
3. Jaw Exercises: Perform gentle jaw exercises to improve strength and flexibility, which can enhance the connection.
4. Avoid Grinding: If you grind your teeth, consider a mouthguard to prevent wear and tear on the teeth and jaw.
5. Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist for professional cleanings and assessments to address any issues early.
6. Orthodontic Treatment: If misalignment is a concern, braces or aligners can improve your bite and strengthen the connection.
What treatments exist for loose teeth due to jaw issues?
Treatments for loose teeth due to jaw issues include:
1. Dental Splinting: Stabilizes loose teeth by using a splint to connect them to adjacent teeth.
2. Orthodontic Treatment: Aligns teeth and jaws to reduce stress on loose teeth.
3. Jaw Surgery: Corrects structural problems in the jaw that contribute to tooth looseness.
4. Bone Grafting: Restores bone density around the tooth roots for better support.
5. Periodontal Therapy: Addresses gum disease to strengthen the supporting structures of teeth.
6. Occlusal Adjustment: Modifies bite alignment to relieve pressure on loose teeth.
Consult a dentist for a tailored treatment plan based on the specific jaw issue.
How do dental implants connect to the jawbone?
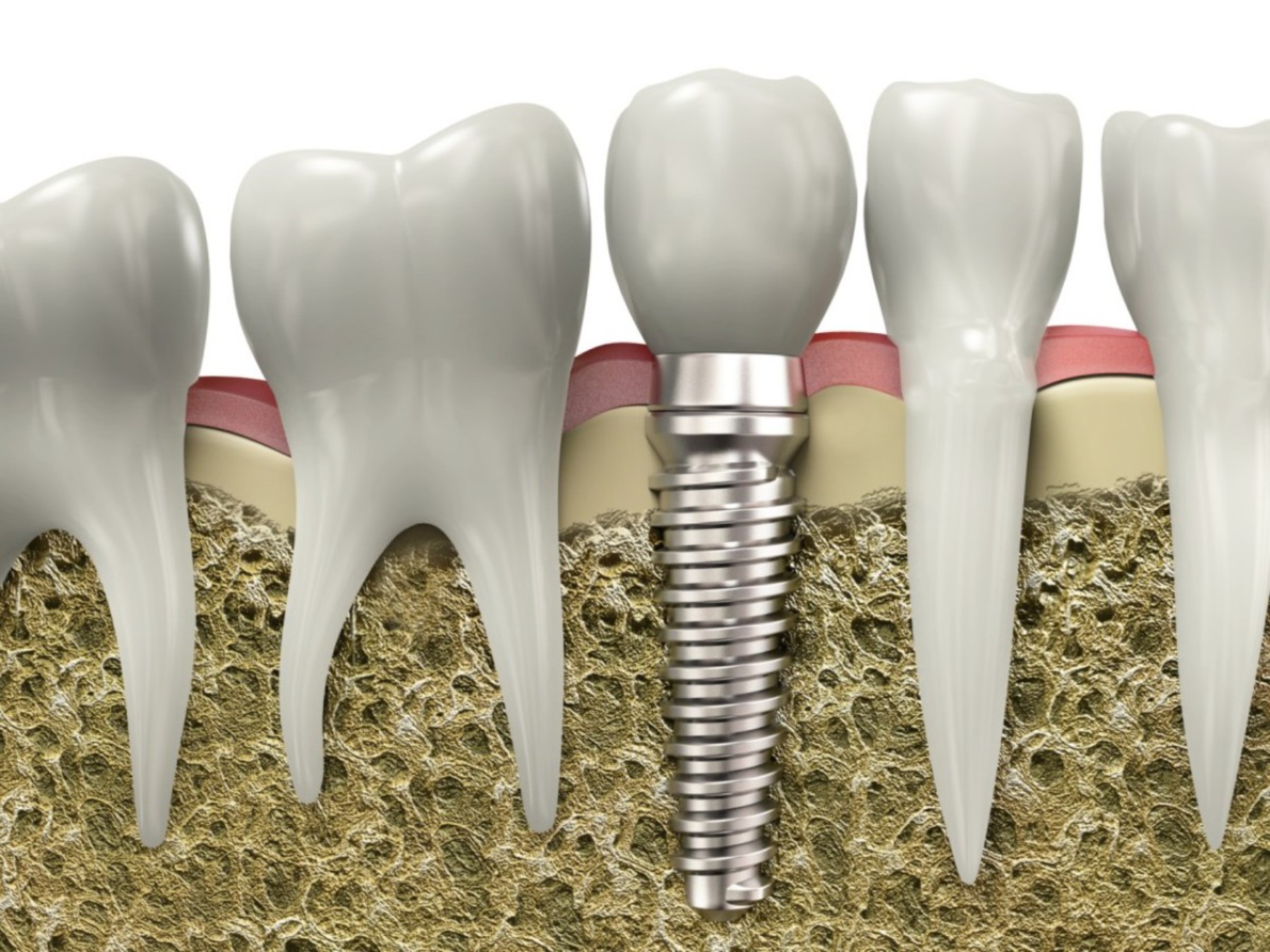
Dental implants connect to the jawbone through a process called osseointegration. This involves the implant, typically made of titanium, being surgically placed into the jawbone, where it fuses with the bone over time. This secure connection provides a stable foundation for replacement teeth.
What is the impact of jaw injuries on teeth?
Jaw injuries can lead to misalignment of teeth, increased wear, fractures, and potential tooth loss. They may also affect the jaw's ability to support teeth properly, causing issues with bite and oral function. Additionally, jaw injuries can result in pain that may limit jaw movement, further impacting dental health and hygiene.
How do nutrition and jaw health relate to teeth attachment?
Nutrition plays a crucial role in jaw health, which directly affects teeth attachment. Adequate nutrients, especially calcium and vitamin D, strengthen bone density in the jaw, promoting stable tooth anchorage. A balanced diet supports periodontal health, reducing inflammation and improving gum attachment to teeth. Conversely, poor nutrition can lead to weakened jawbone and gum issues, compromising the stability and attachment of teeth.
Conclusion about # How Are Teeth Connected to the Jaw?
In summary, the connection between teeth and the jaw is crucial for overall oral health. Understanding how teeth are anchored to the jawbone, the role of the periodontal ligament, and the impact of alignment can help prevent dental issues. Maintaining bone density, recognizing signs of unhealthy connections, and addressing jaw problems are essential for sustaining strong teeth. For more comprehensive insights and solutions regarding tooth and jaw health, consider seeking information from Tooth1.